Important characteristics of the alkanols homologous series;
CnH2n+1OH
There are three categories of alcohol - primary, secondary and tertieary.
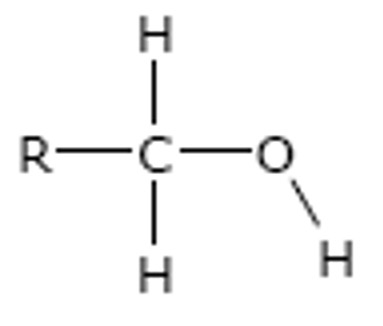
Primary
The carbon attached to the -OH group is directly bonded to only one alkyl group. (i.e. 1 carbon)
e.g.
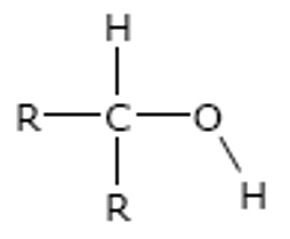
Secondary
The carbon attached to the -OH group is directly bonded to two alkyl groups. (i.e. 2 carbons)
e.g.
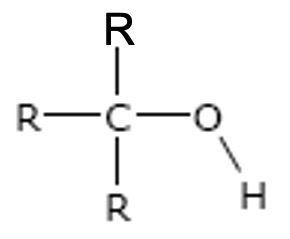
Tertiary
The carbon attached to the -OH group is directly bonded to three alkyl groups. (i.e. 3 carbons)
e.g.
Isomers can result from both chain branching and varying the position of the -OH group.
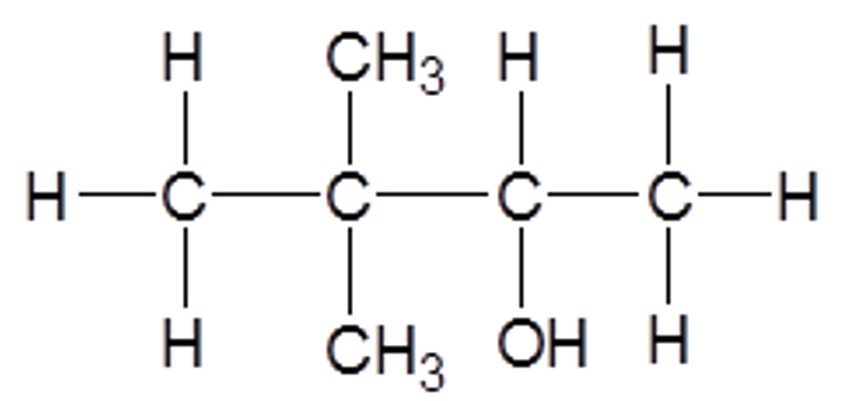
Name the molecule below.