

Copy the table below into your notes
| Angle of Incidence | Angel of reflection |
|---|---|
Collect the following equipment:
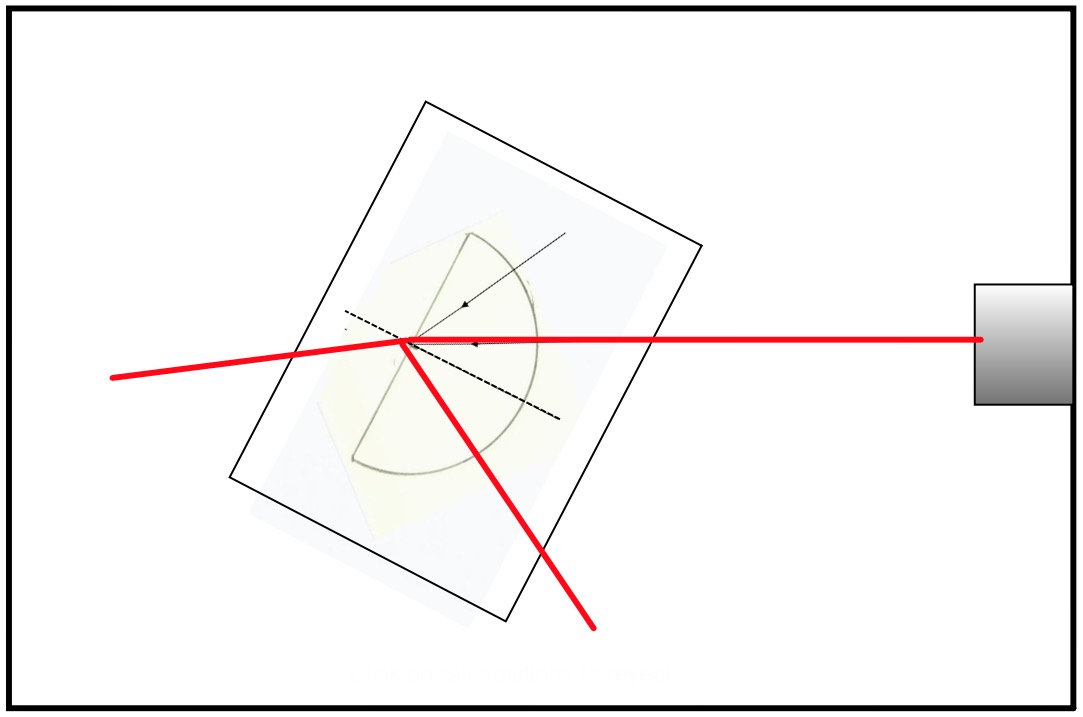
Set the equipment up as shown below:
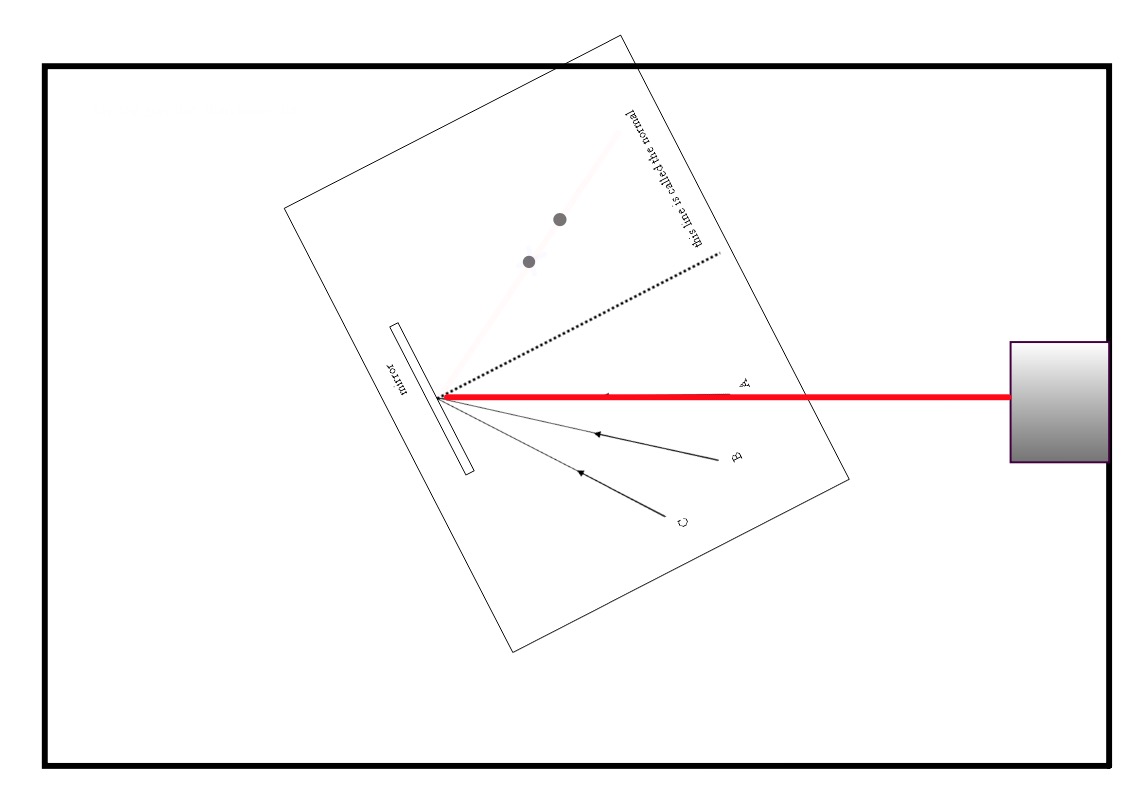
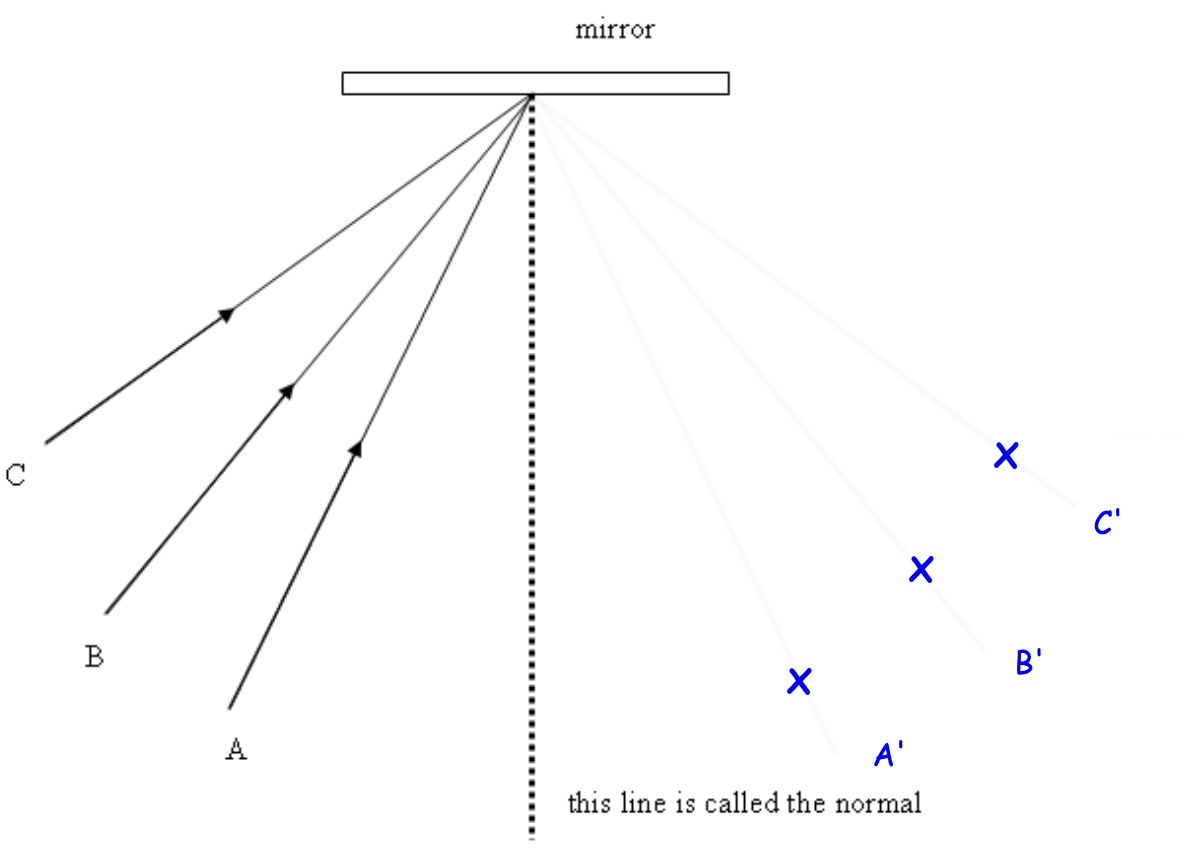
Label the X's A', B' and C', and draw line through them from the reflecting point.
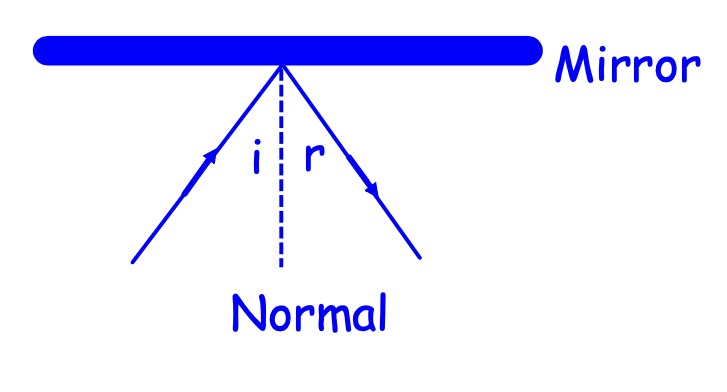
angle of incidence = angle of reflection

Light is a type of wave. It can pass through substances such as g____ and w____. A substance which it can pass through is called a medium. (Plural is media)
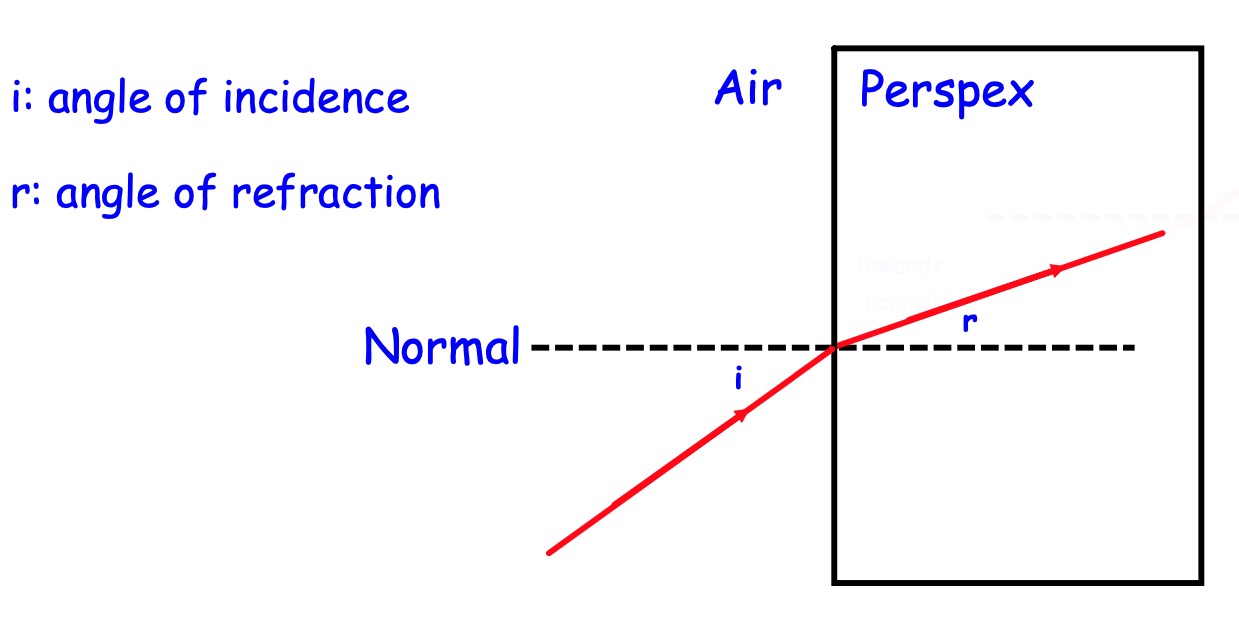
Refraction is when light changes direction as it passes through another material. Light does this because it slows down when it enters the material.
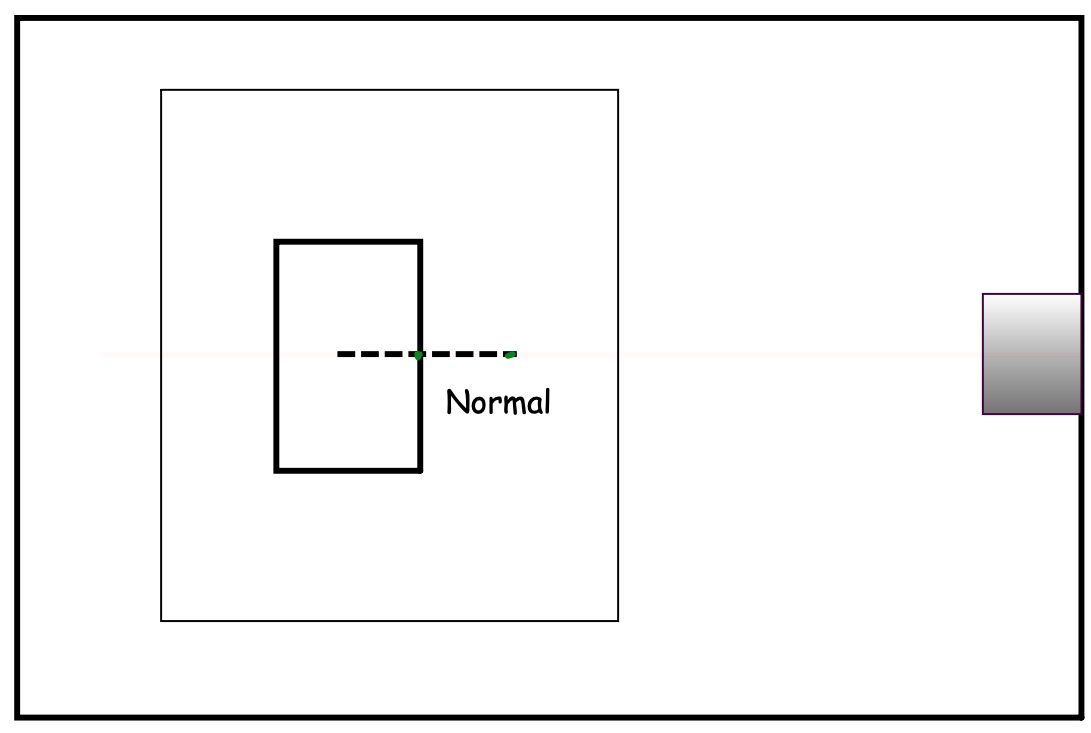
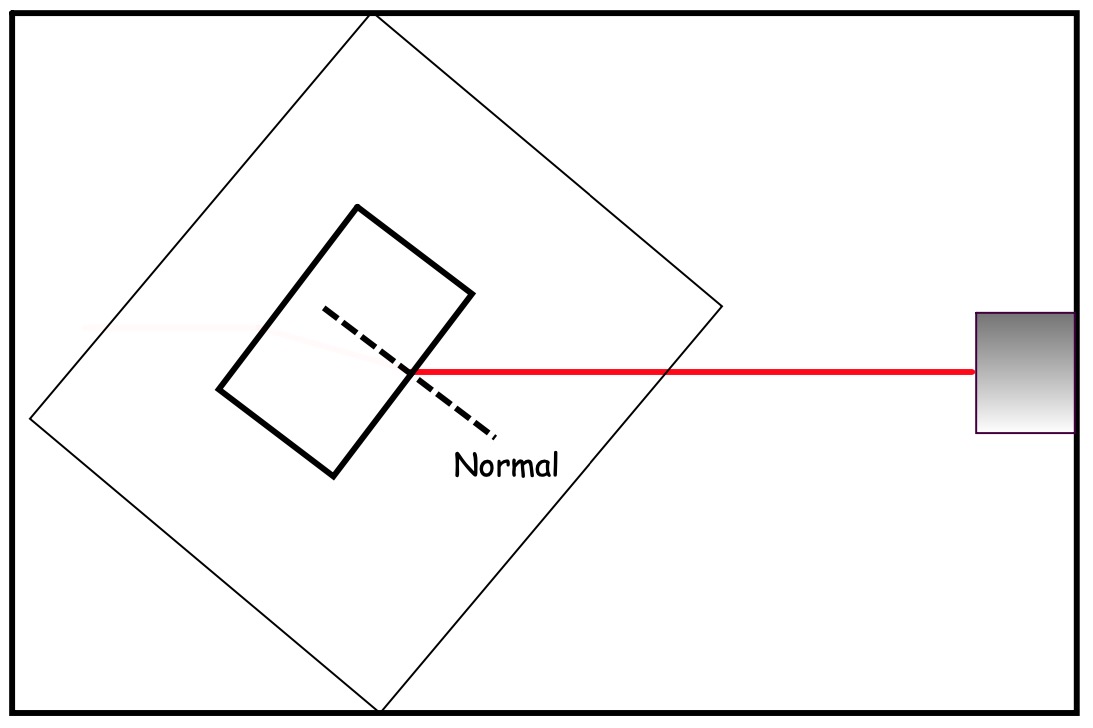
Tilt the paper with the block in place as in the diagram.
Mark on the paper where the ray goes in and comes out the block, and a few centimetres along the ray.
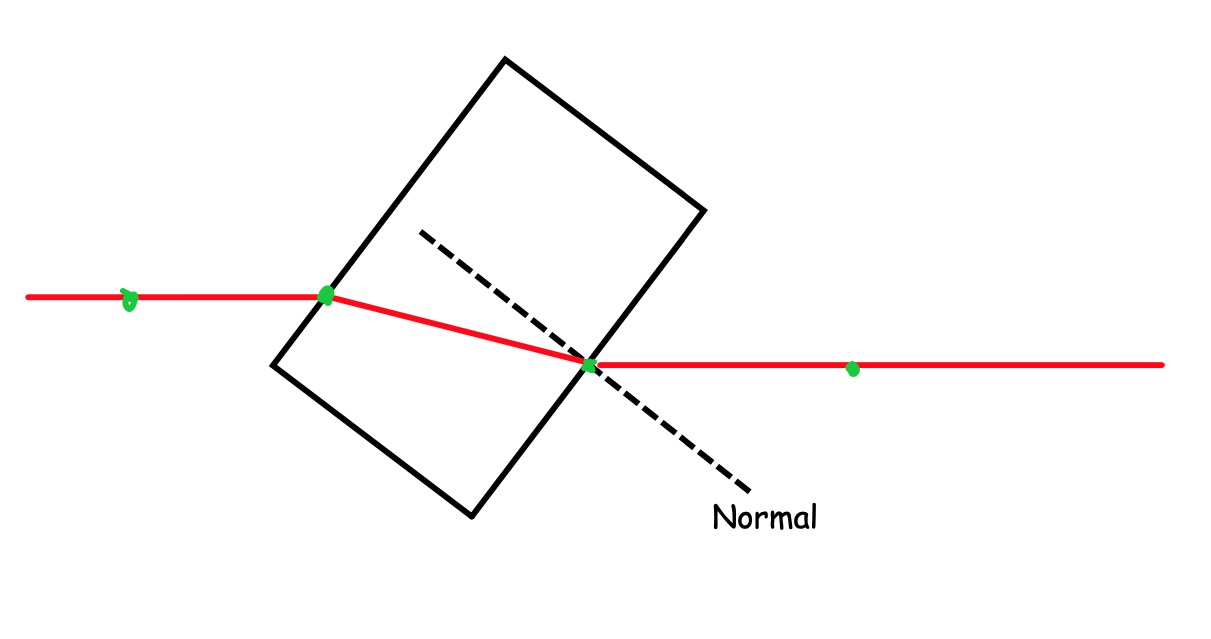
Remove the block, and draw in the rays using the points you've marked.
Refraction is when light changes speed and direction when going from one material to another.
Split into pairs.
Person A and Person B
Person A collect a cup and a coin from the trolley
Person B collect a glass beaker nearly full of water
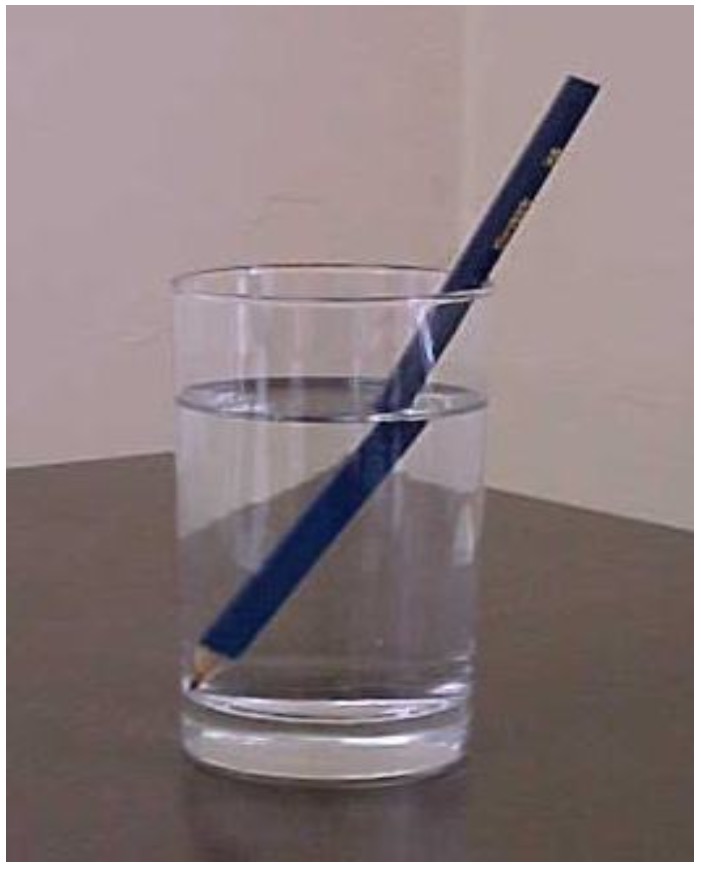
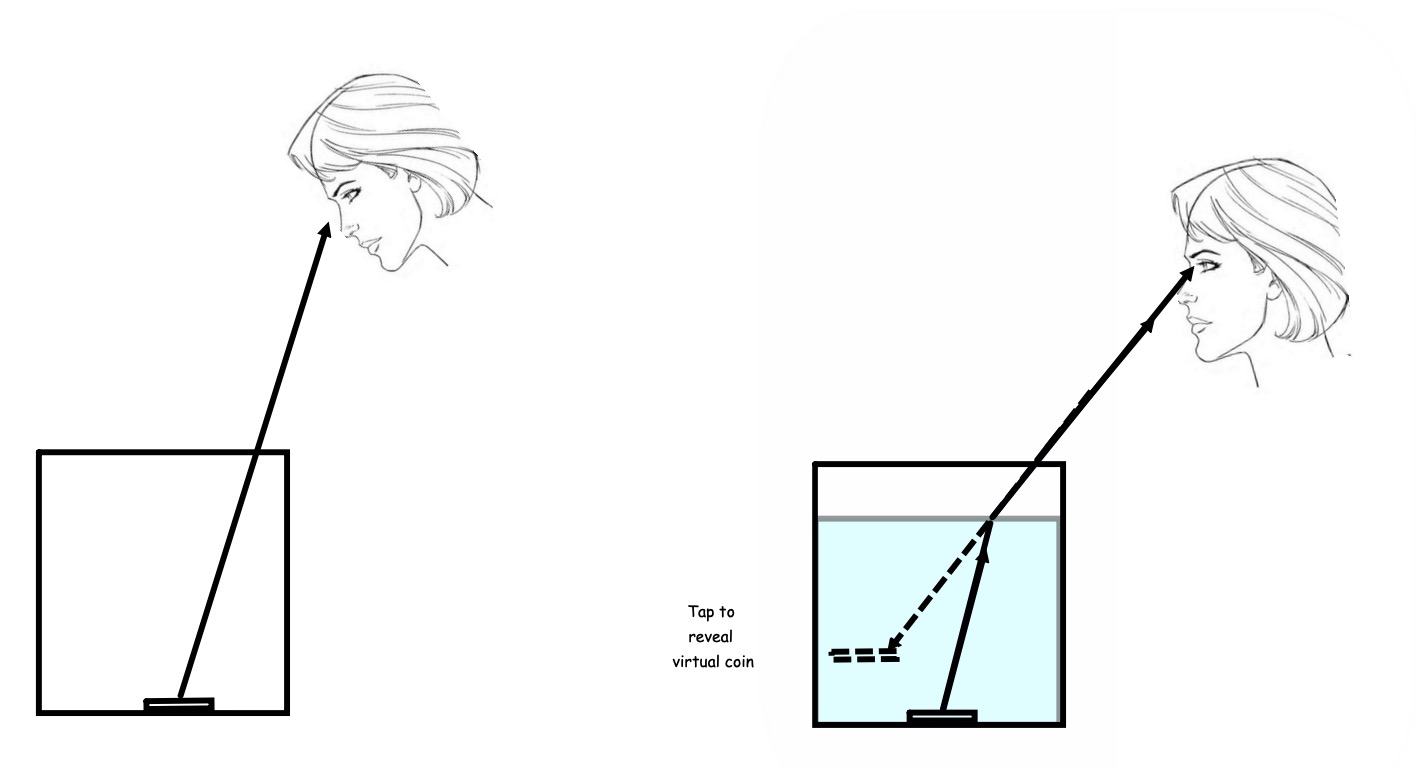
Person A Put the coin in the cup and put it on a bench. Lower your head down until you JUST stop seeing the coin. Keep your head in that position!
Person B pour the water into the metal beaker slowly, taking care not to move the coin!
Person A What do you see?
Swap and do the experiment again!
On a blank piece of paper, draw a straight line using a ruler.
Draw round a lens so that it's at right angles to the line.
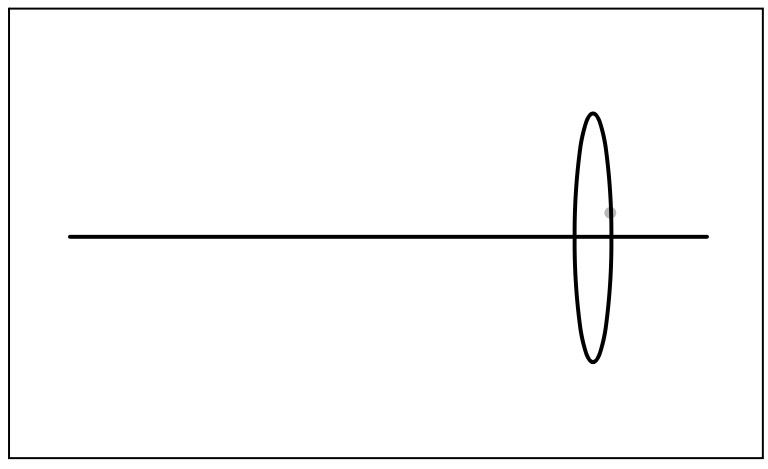
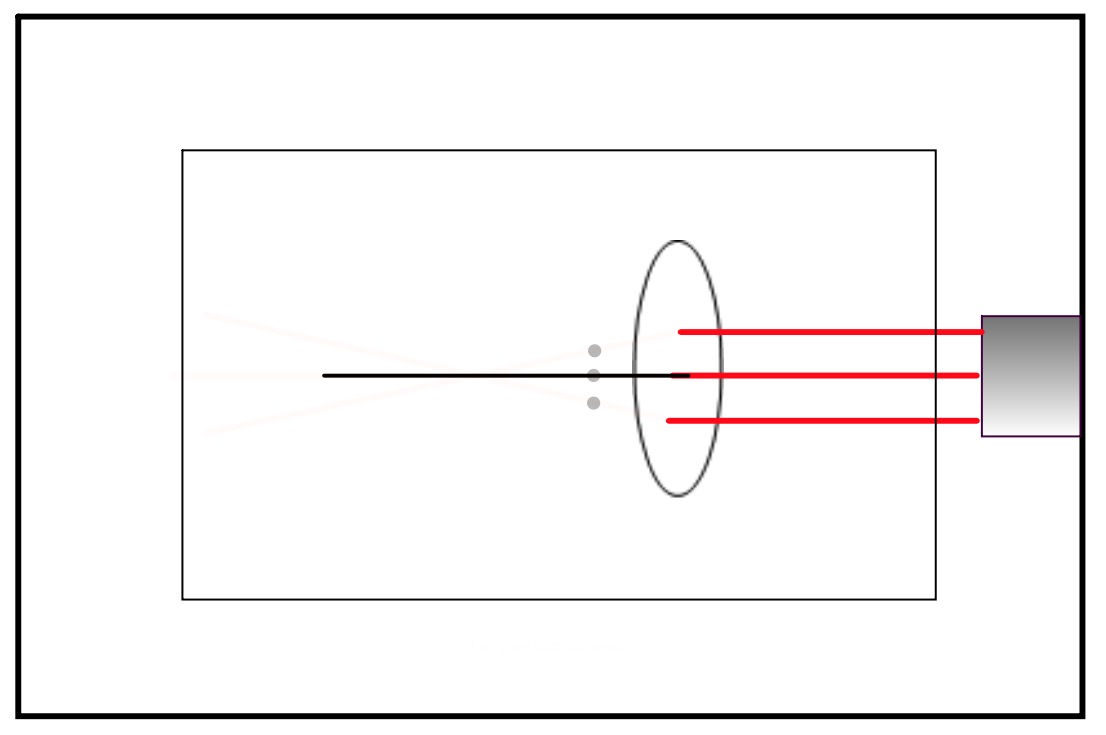
Put your diagram on the laser board so the middle ray goes along the straight line.
Place the lens on the outline.
Complete a copy of the handout below and stick into your notes.
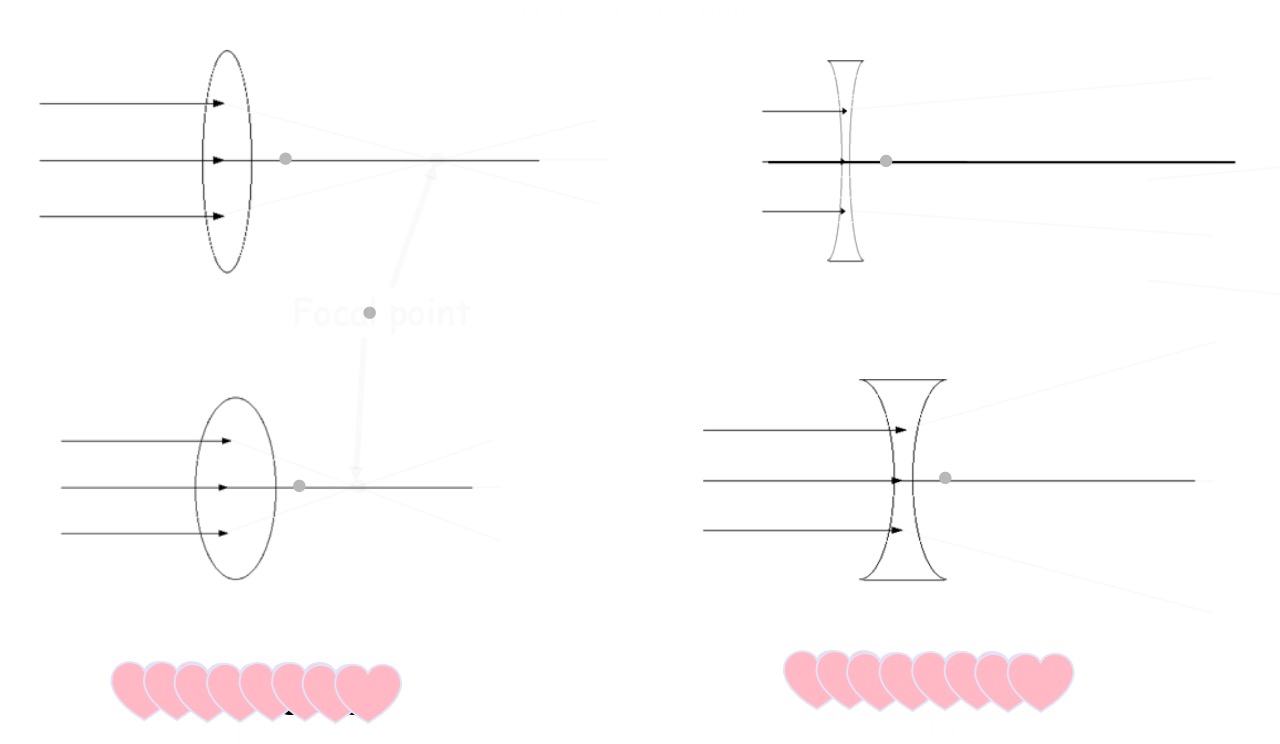
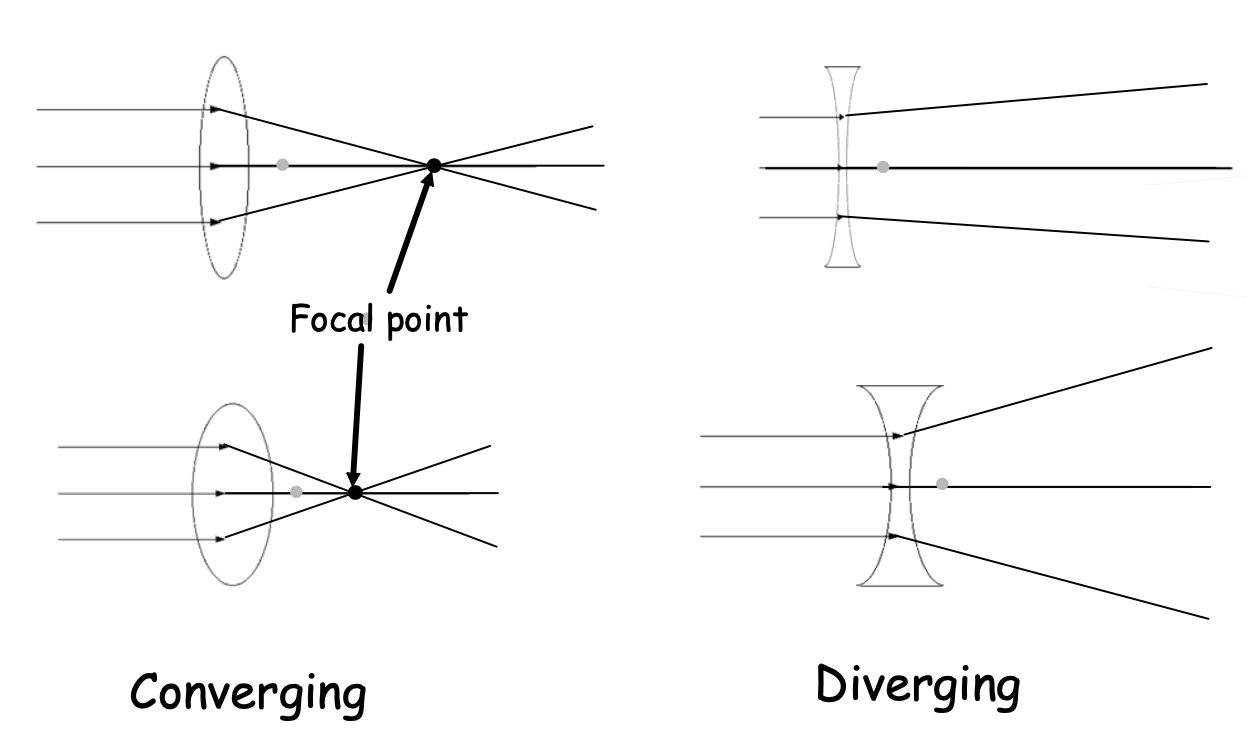
As you get older, your sight usually gets worse. There's not much you can do to stop this happening - it's a condition called middle aged presbyopia.
So if you don't wear glasses already, you probably will when you're older. So how do glasses work to correct our sight?
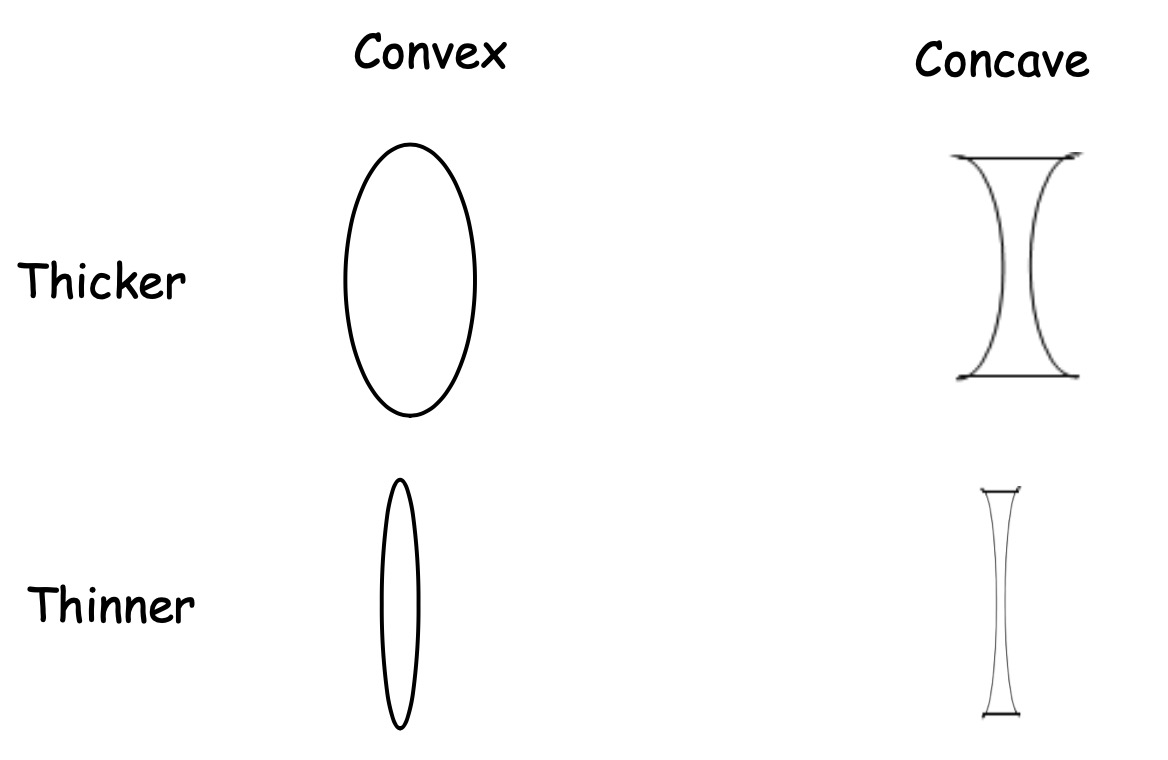
The two pieces of glass or plastic in front of your eyes are called lenses. Lenses turn up all over the place - in telescopes, for example.
Questions
1. What is the name of the condition that causes sight problems as you get older?
2. List three things, not mentioned above, that use lenses.
3.Name the two main types of lens.
4.What are the other names for the lenses?
Mark small crosses on the paper where the rays emerge from the block.
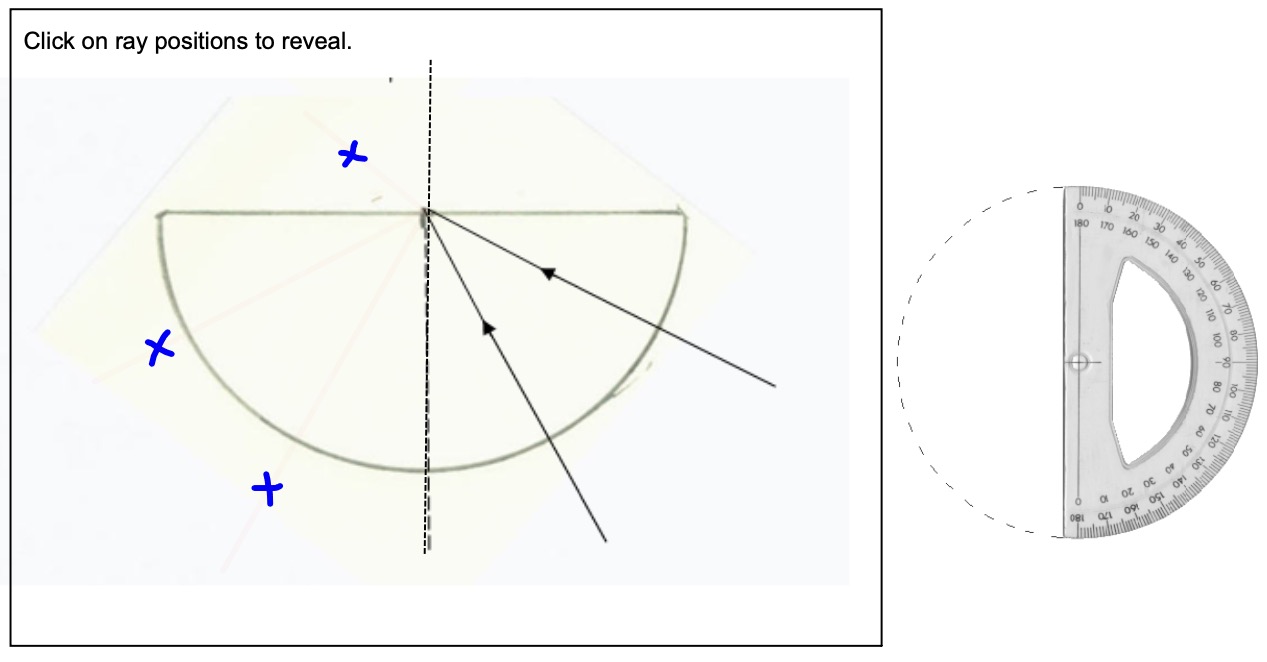
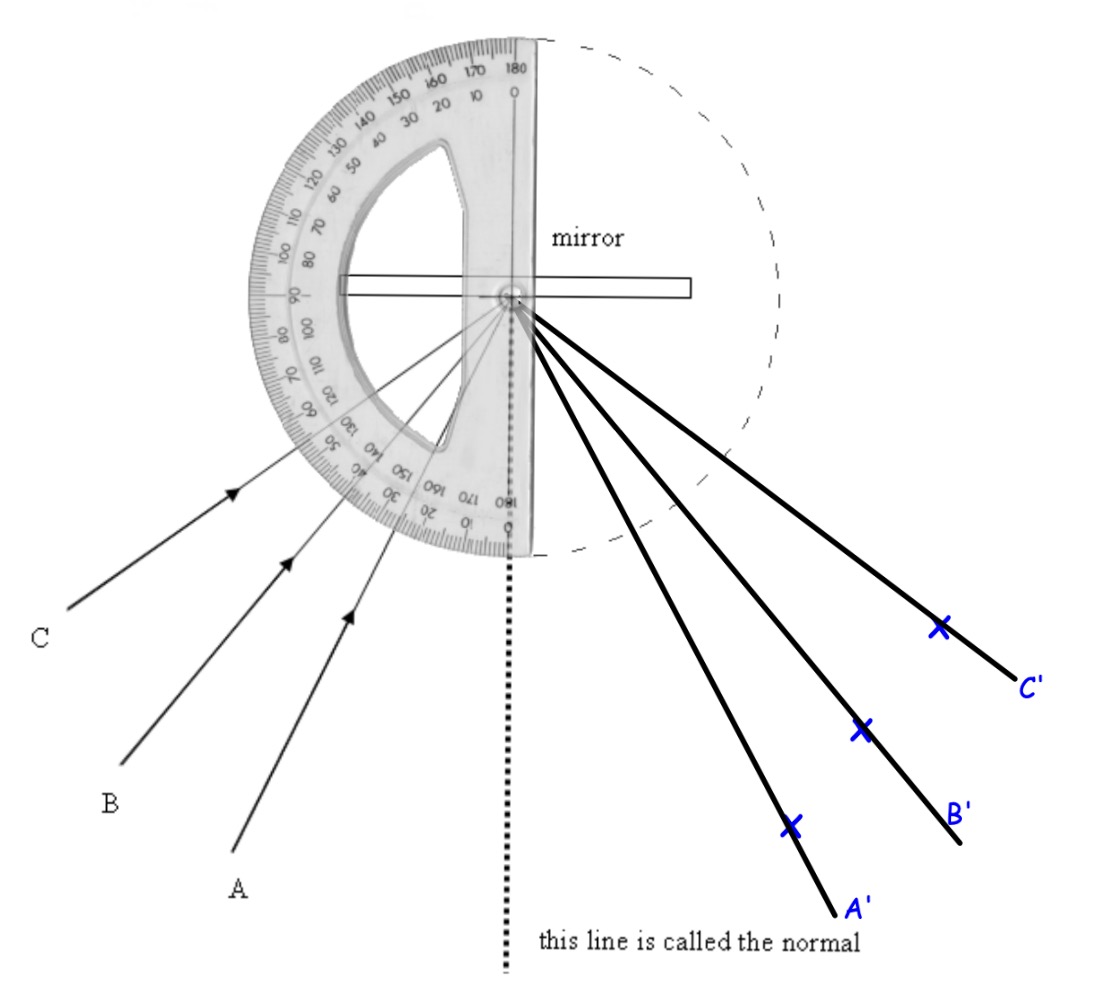
Use a protractor to measure:
The smallest angle of incidence for which the ray is totally reflected is called the critical angle. When all the light is reflected, it is called Total Internal Reflection.
Copy this diagram showing the path of the ray of light in the optical fibre.
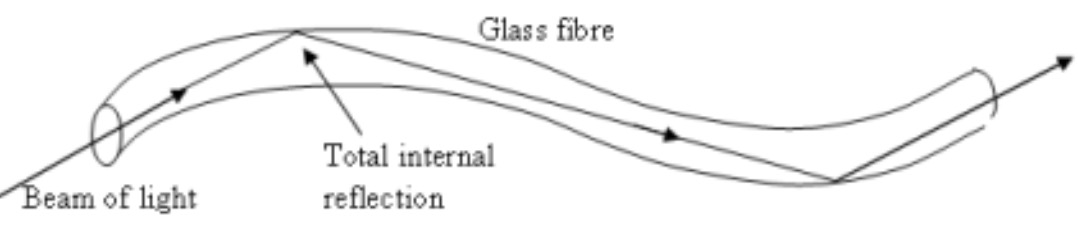
Do you know what optical fibres are used for?
You'll need a ray box with a single slit, a power supply, a triangular prism and a screen made of white card.
Set up your equipment like this.
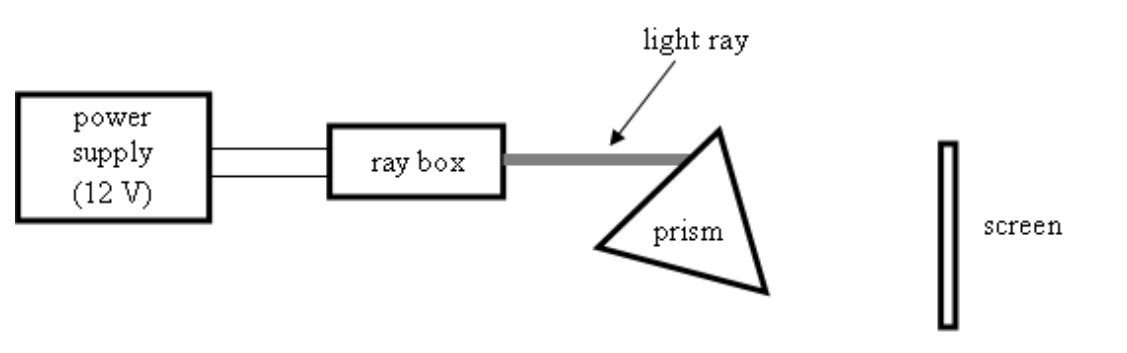
Point the light ray near the top corner of the prism. Now turn the prism slowly, keeping an eye on the screen.
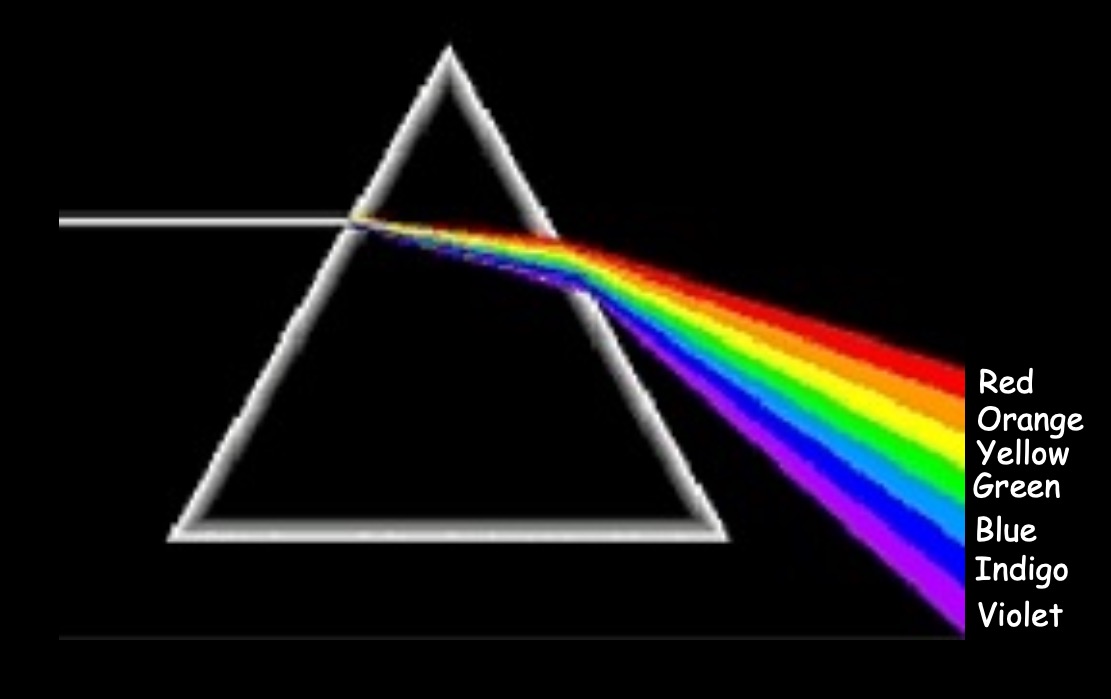
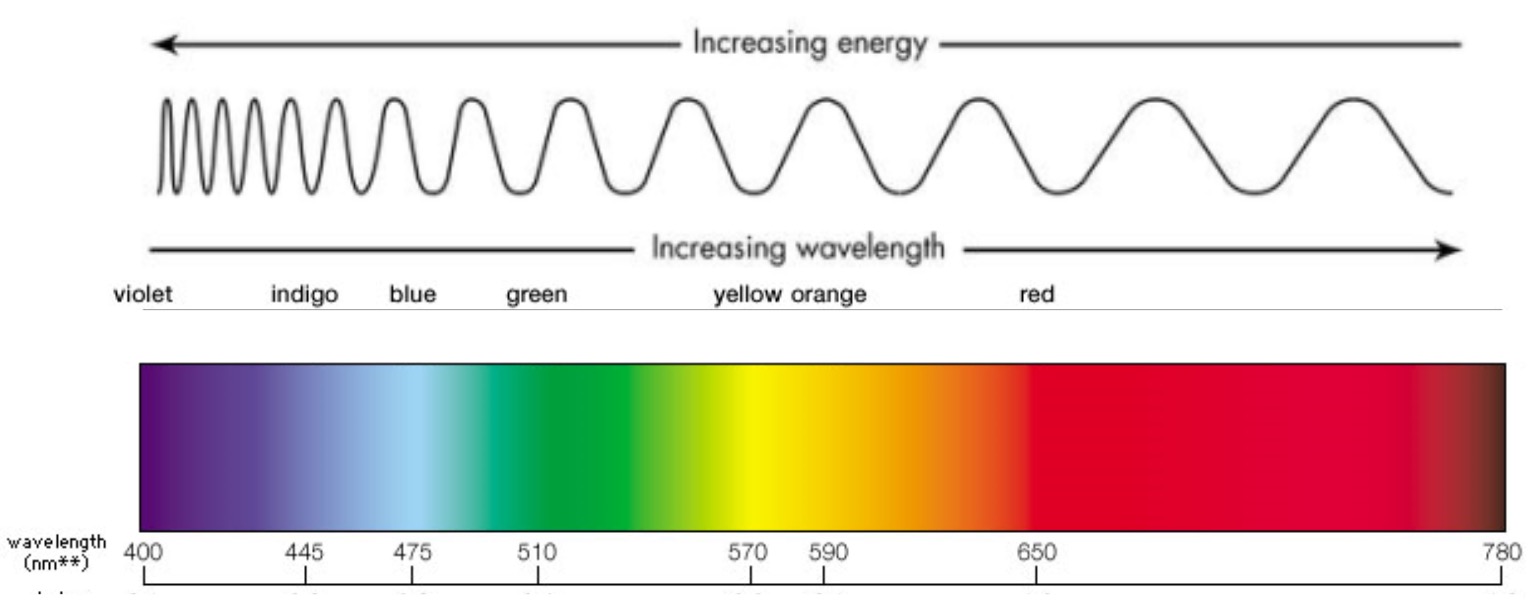
White light contains all of the colours and produces a continuous spectrum.
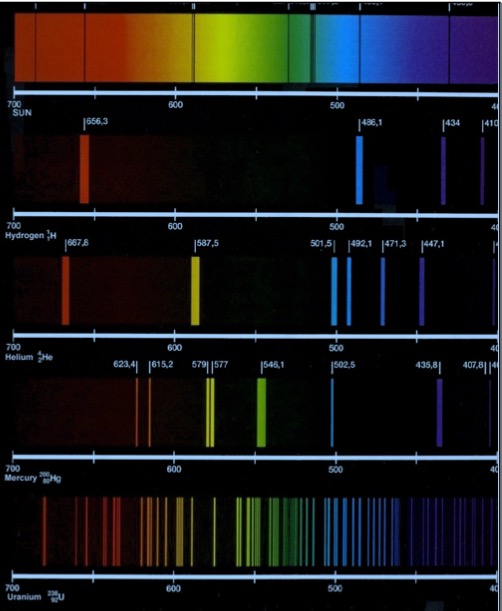
Collect a spectroscope and look at some light sources.


Rainbows form due to refraction and reflection of light in rain droplets. It only happens at certain angles and the sun has to be in the perfect position.
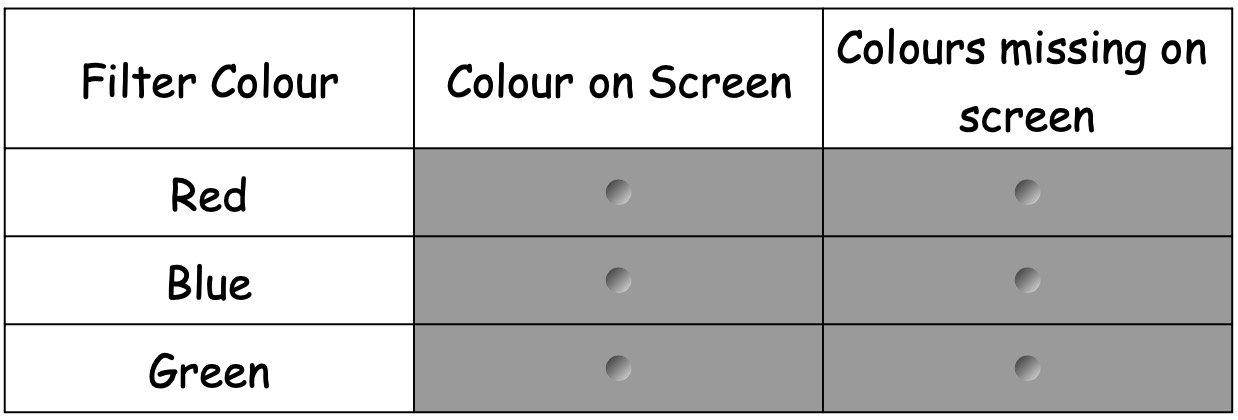
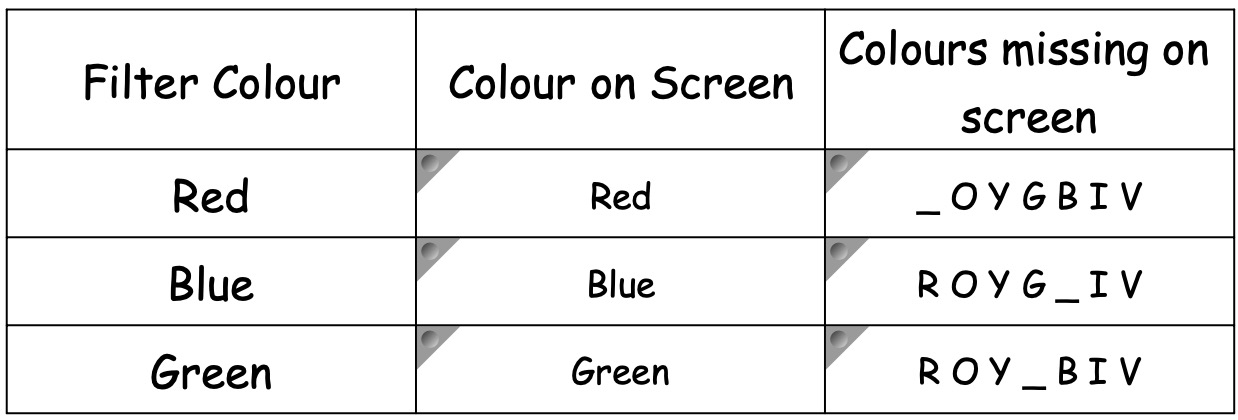
Collect a set of coloured filters.
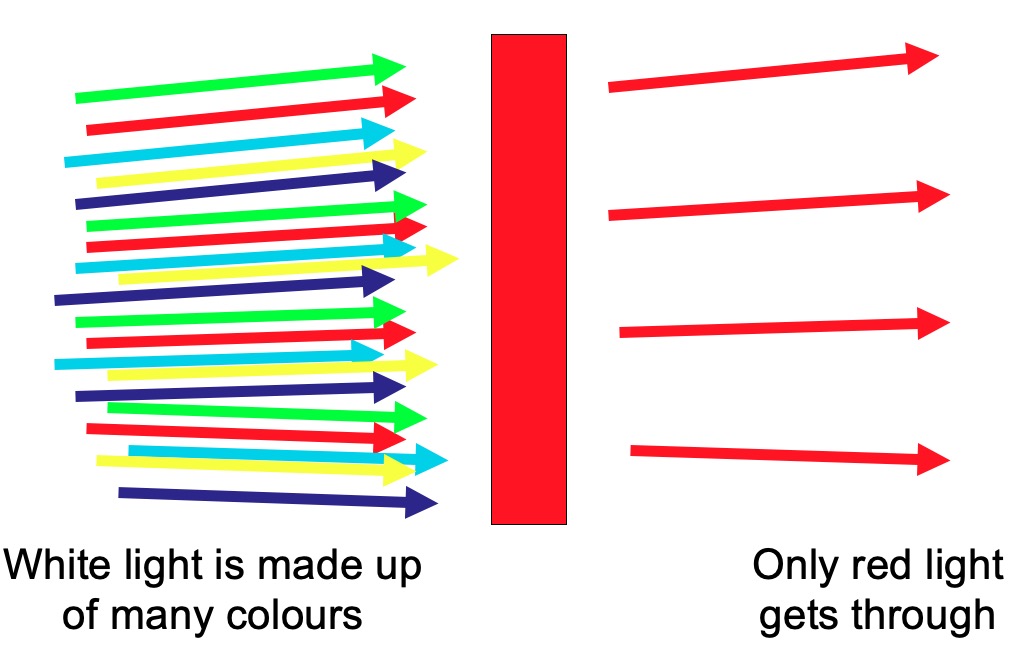
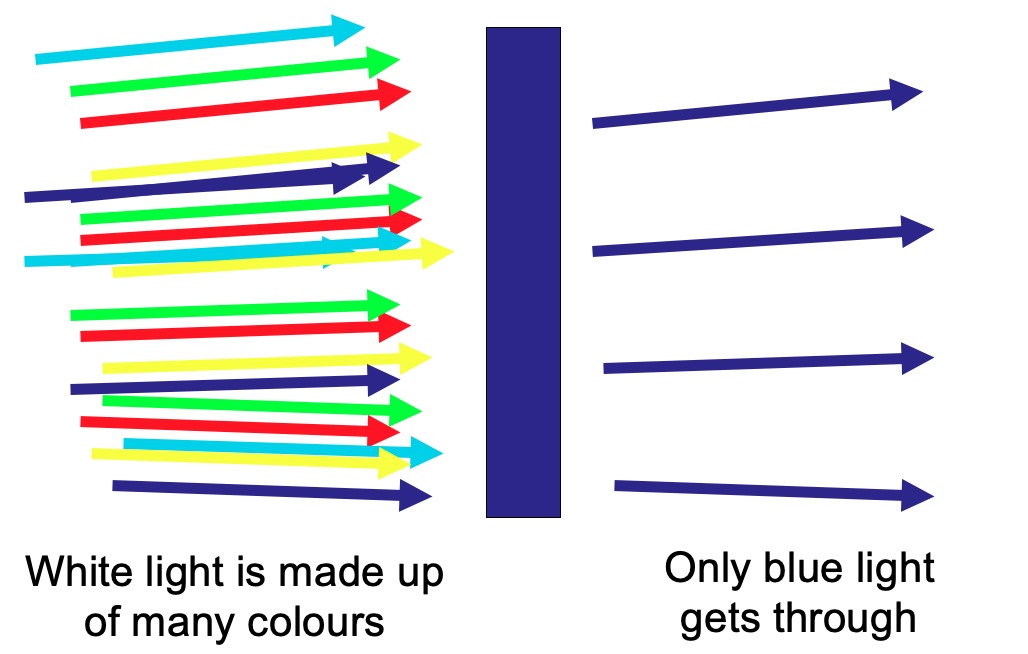
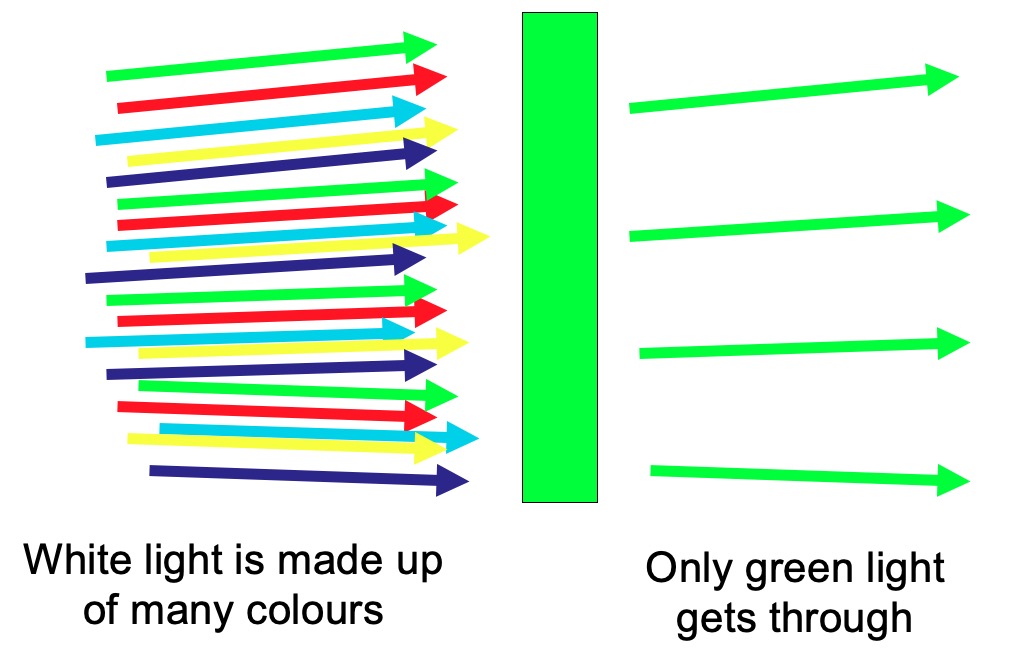





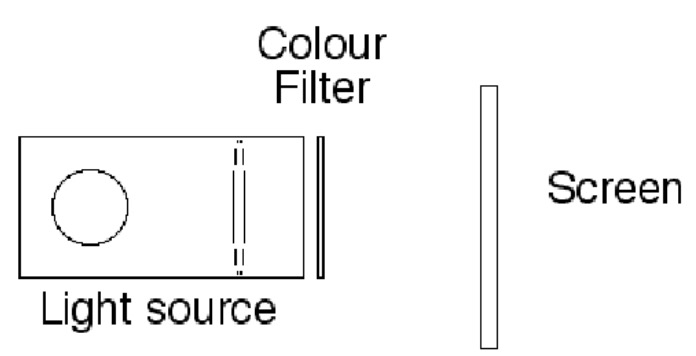
Using your knowledge of white light, identify what colours must be missing on the screen with each of the filters.
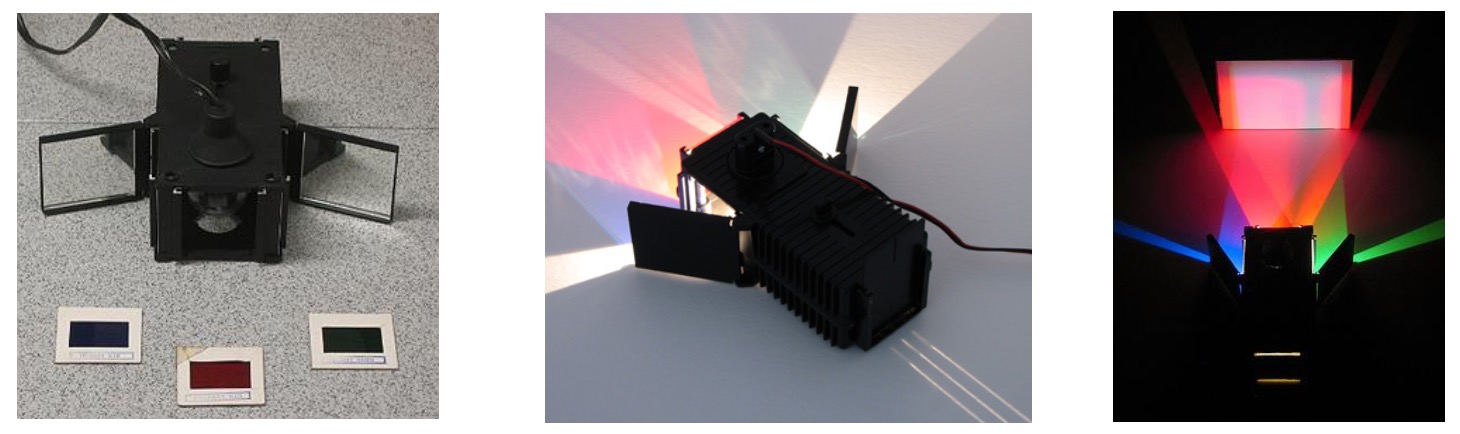
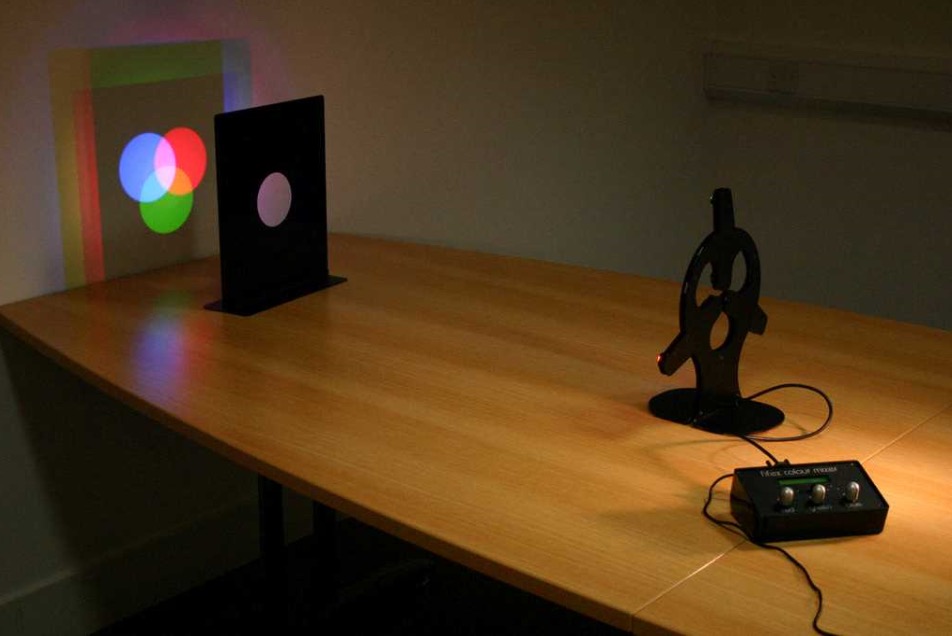
Collect the colour mixing apparatus
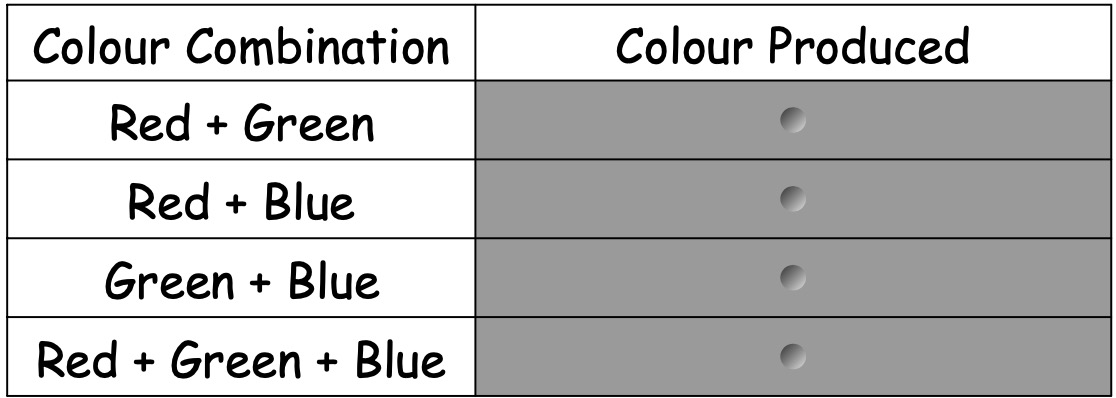
Copy and complete the table below into your notes
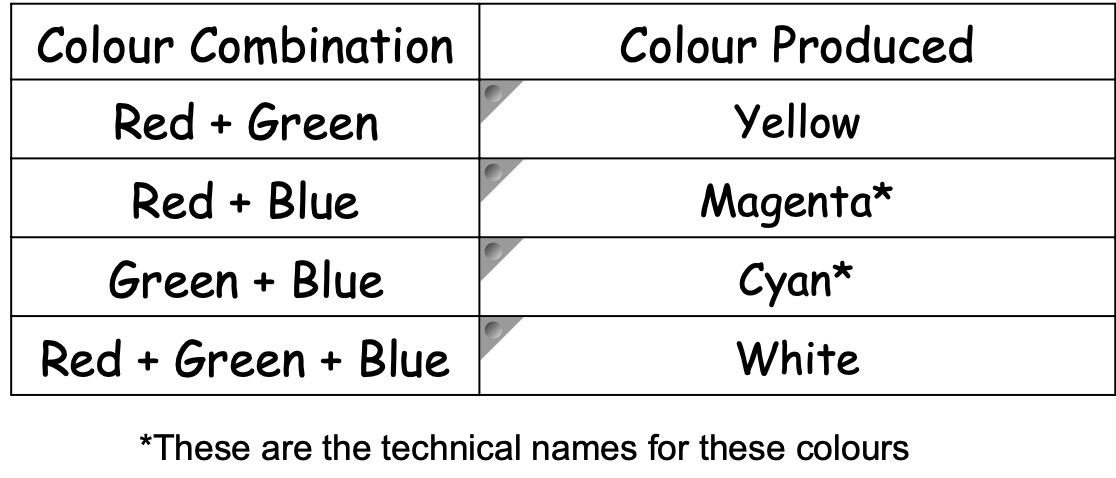
Watch your teacher demonstrate colour mixing or click on the picture below to take you to a simulation.


How many colours can you see in the picture below?




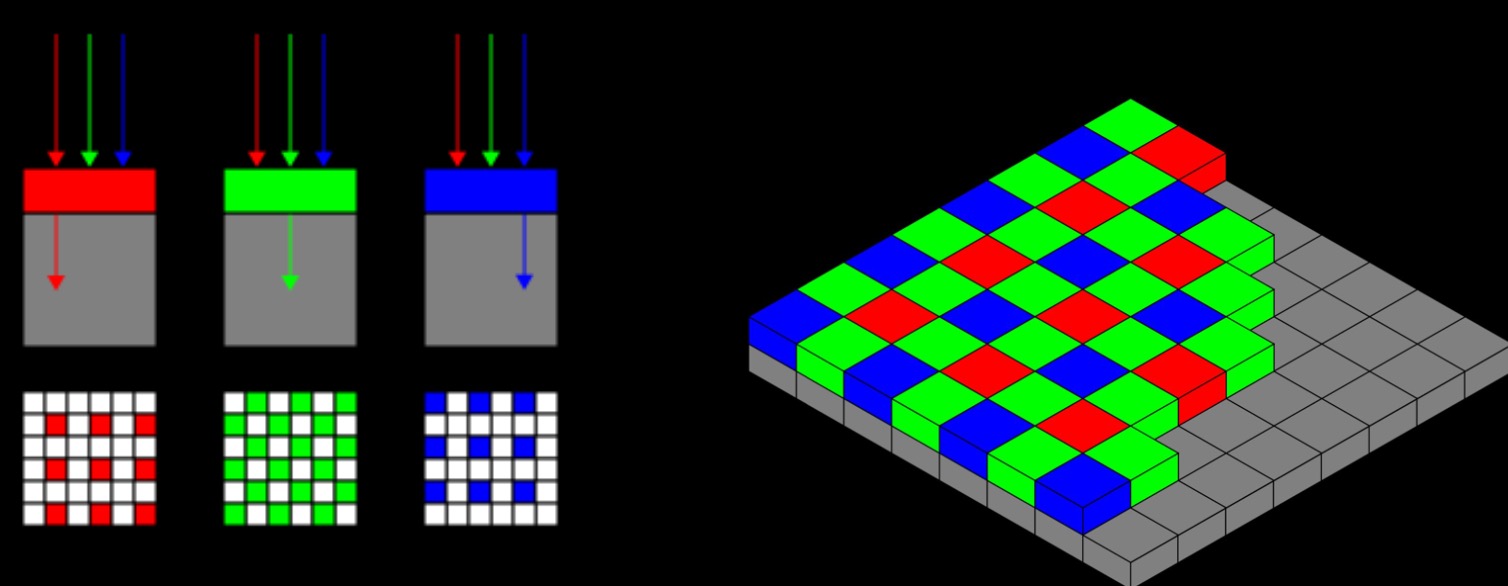
The camera on your phone actually only "sees" in black and white.
Each time it takes a picture, it is really taking three simultaneously; one each through red, green and blue filters.
Clever electronics then recreate a single colour image.
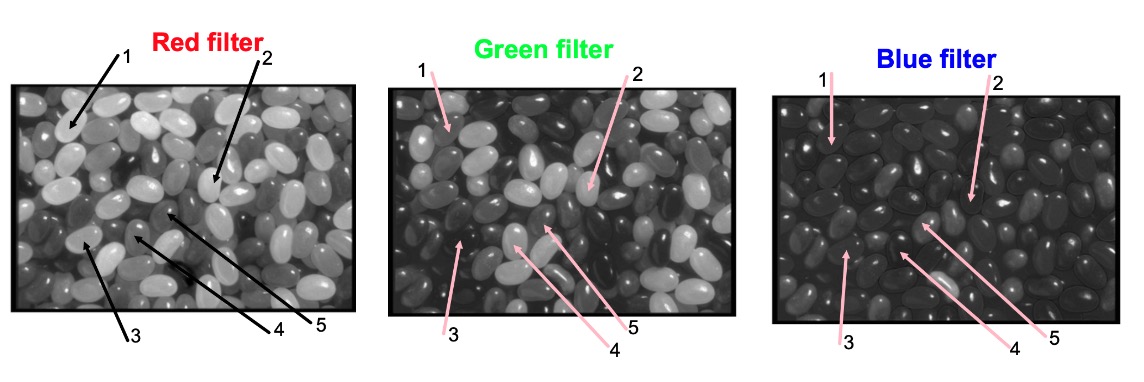
Look at this colour square through first RED then GREEN and finally BLUE filters.
Record on the appropriate table whether each square appears BRIGHT,MID or DARK.

Decide whether the beans are bright, mid or dark and match up with the results from your grids.
Were you right?
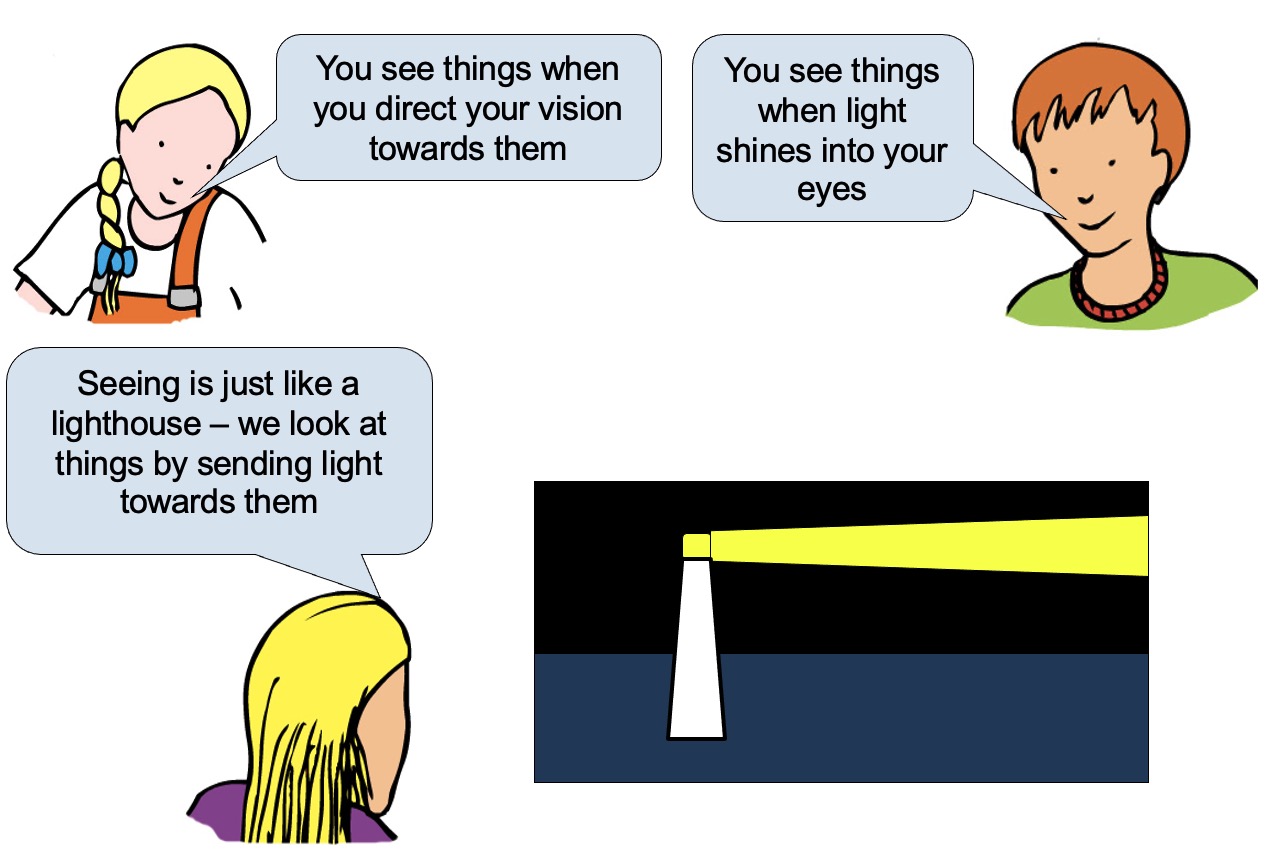
Light, sound, x-rays, radio signals all travel as waves.
Before we look at waves of different types we must know how to describe waves.
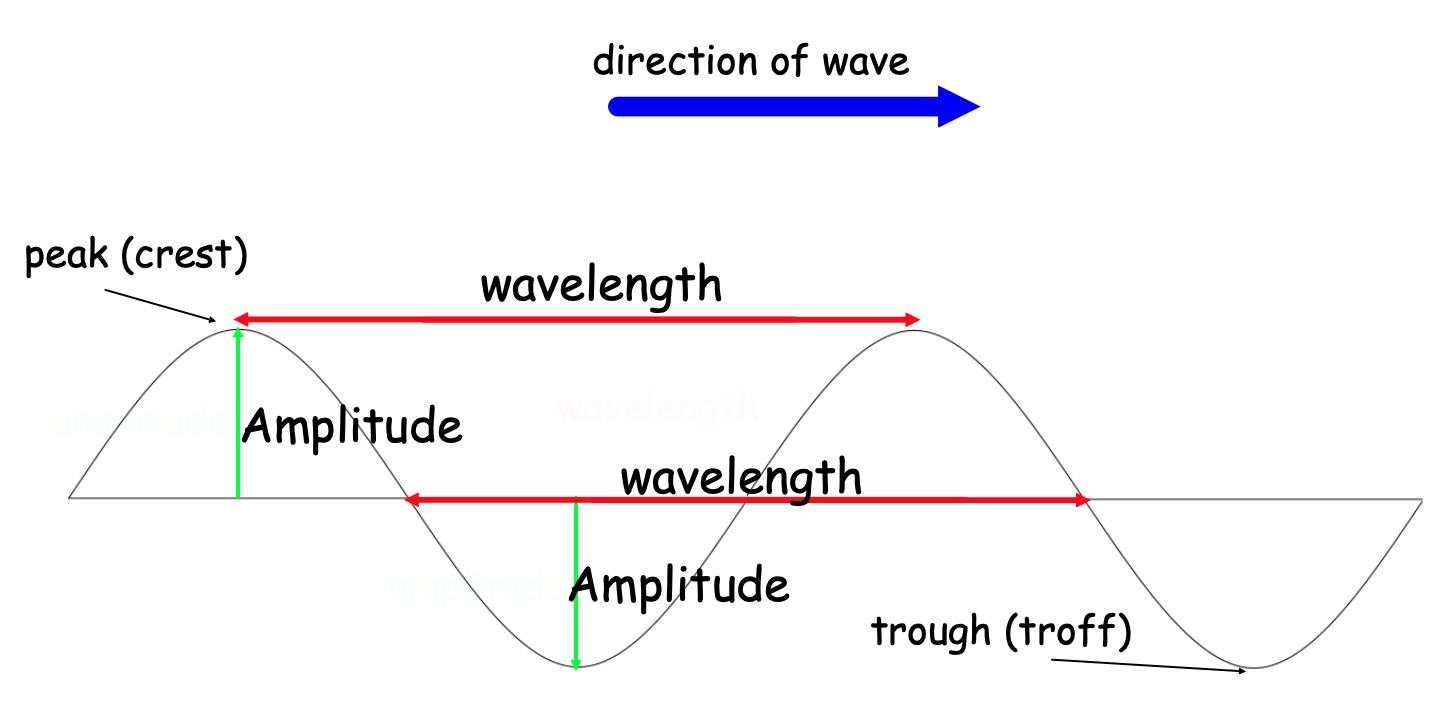
Collect this diagram, label it, and stick it into your jotter.
The number of waves that pass a point every second is called the frequency.
For light the frequency determines the colour of the wave, and the amplitude determines the brightness.
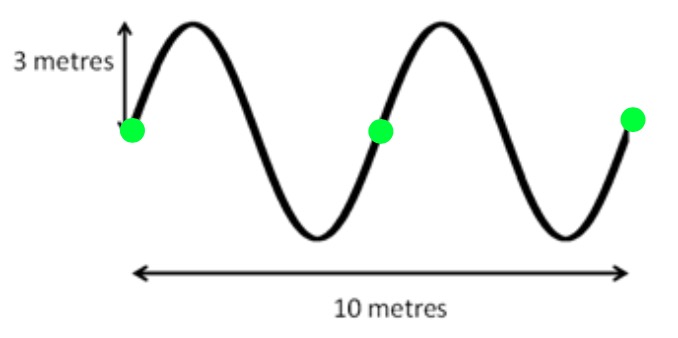
(a) How many complete waves are shown in the diagram above?
(b) What is the wavelength of the wave?
(c) What is the amplitude of the wave?
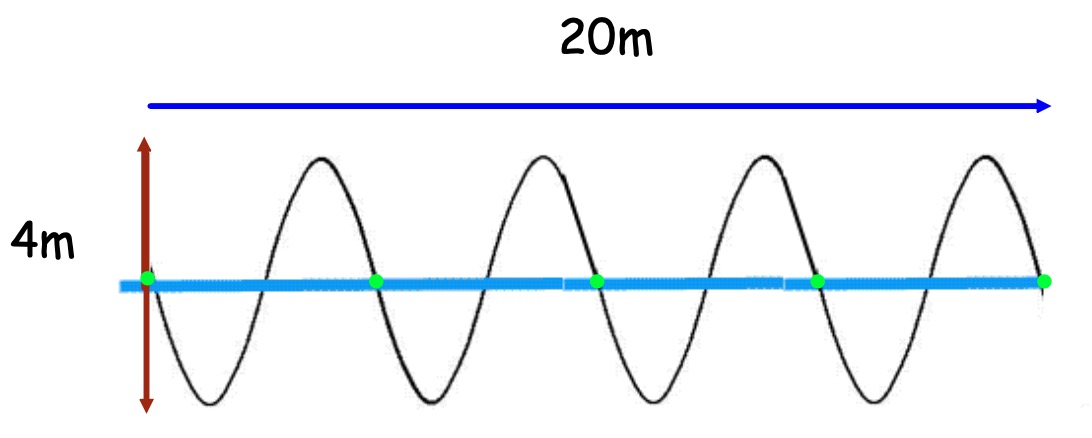
a) How many waves are shown in the diagram above?
b) What is the length of each wave (wavelength)?
c) What is the amplitude of the wave?
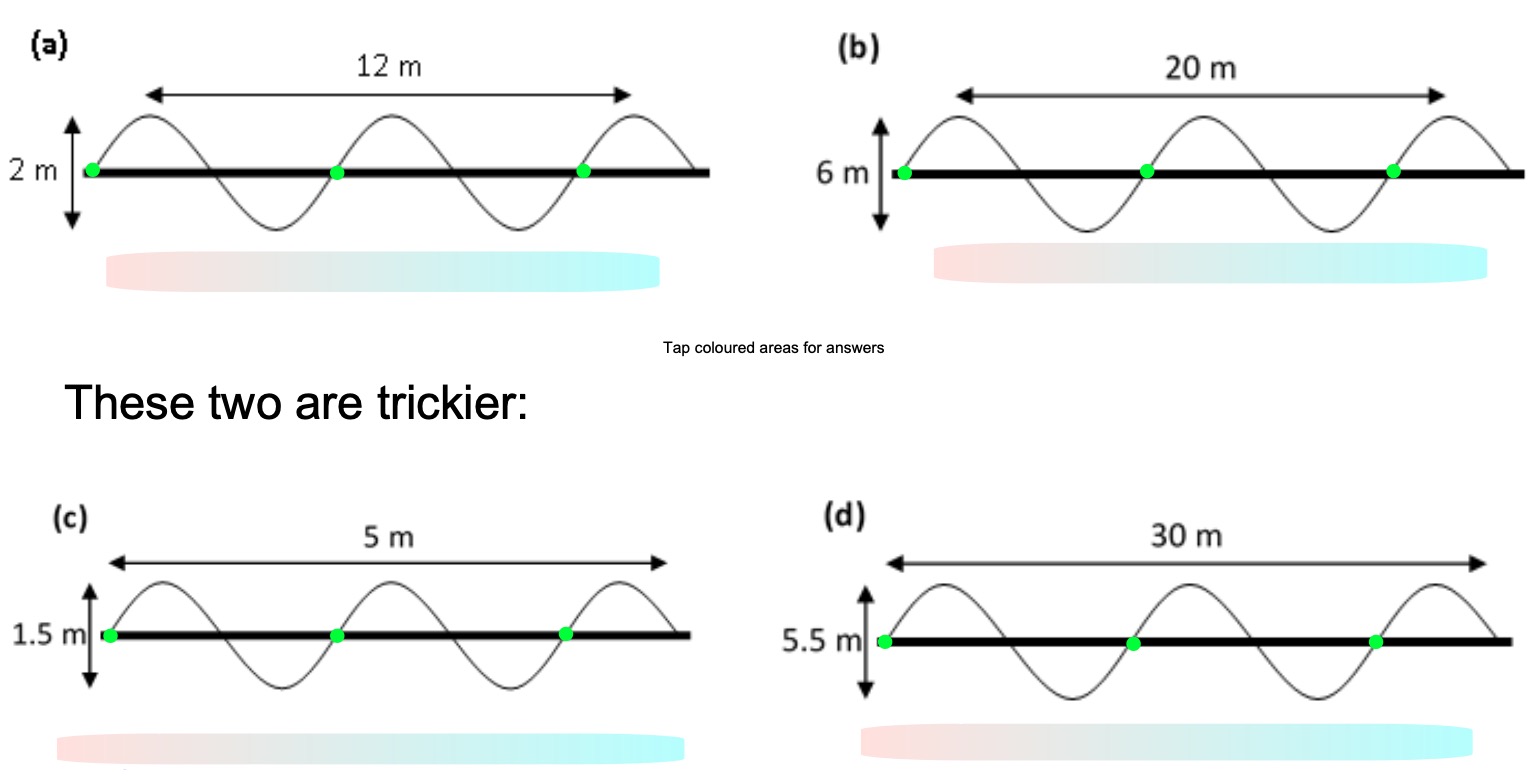
Find the amplitude and wavelength of these waves:
Frequency is the number of times something happens per second. The unit of frequency is hertz (Hz).
1 hertz is 1 per second.
We can use this equation to help us calculate the frequency:
Frequency = Number of waves ÷ Time taken
Four waves are produced in 2 seconds, what is the frequency ?
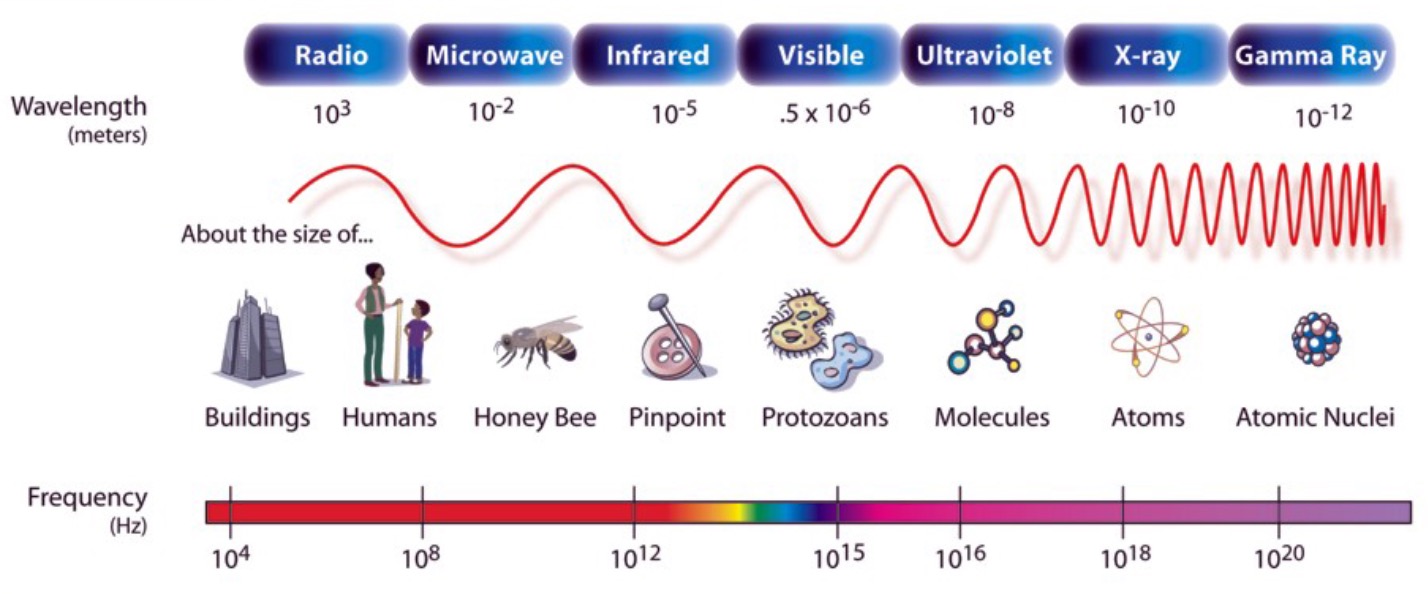
The frequency, wavelength and energy of a wave are all related. As the frequency of a wave increases, the wavelength gets shorter. As there are more waves per second, more energy is transferred.