

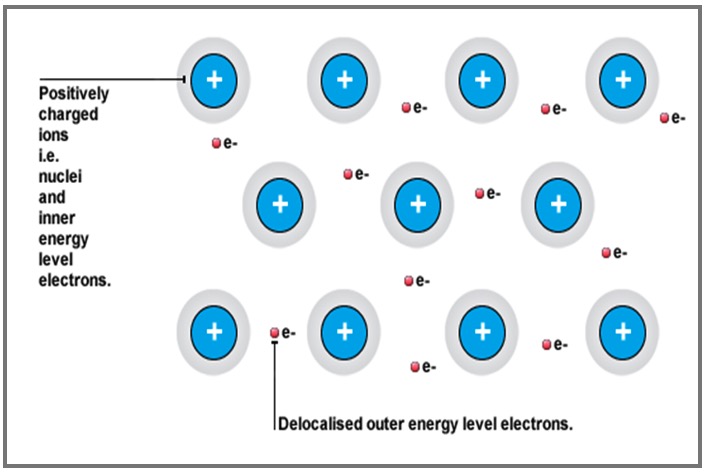
Metallic bonding is the electrostatic force of attraction between positively charged ions and delocalised electrons.
Metallic elements are conductors of electricity because they contain delocalised electrons.
A reactivity series of metals is a table which puts the metals in order of how reactive they are.
The reactivity series is also known as the electrochemical series.
The most reactive metals are at the top and the least reactive are at the bottom.
Metals can be arranged in order of reactivity by comparing the rates at which they react.
metal + oxygen → metal oxide
metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
Metals can be used to produce soluble salts. Excess metal is added to the appropriate acid, the mixture is filtered and the filtrate evaporated to dryness.
metal + oxygen → metal oxide
Example,
magnesium + oxygen → magnesium oxide
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
All of the metals above goldin the reactivity series react with oxygen.
metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
Example,
magnesium + water → magnesium hydroxide + hydrogen
All of the metals above aluminium in the reactivity series react with water. (hint - every metal with m at end !!)
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
Example,
magnesium + hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + hydrogen
All of the metals above hydrogen in the reactivity series react with acid.
The table below shows which metals react with oxygen, water and acid and how the metals can be extracted from their ores.
| metal | extraction method | oxygen | water | acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium | electrolysis |