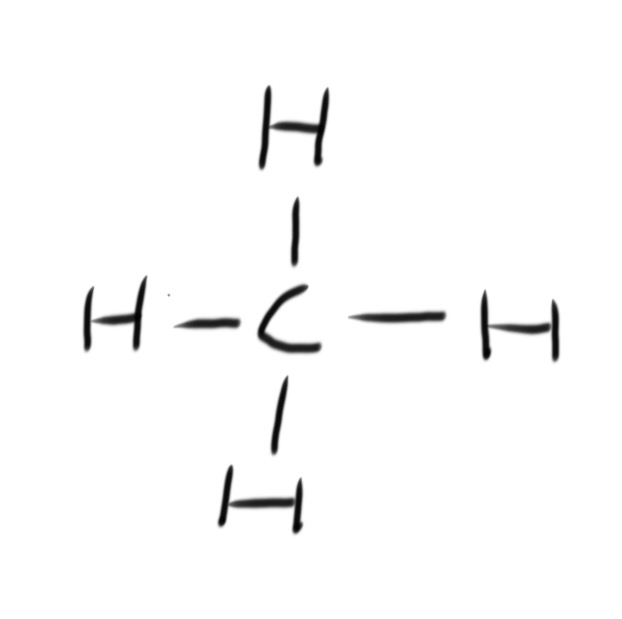
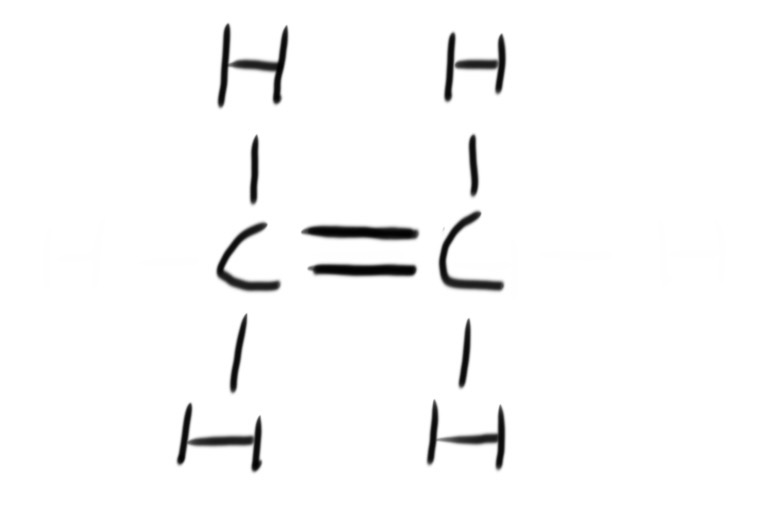
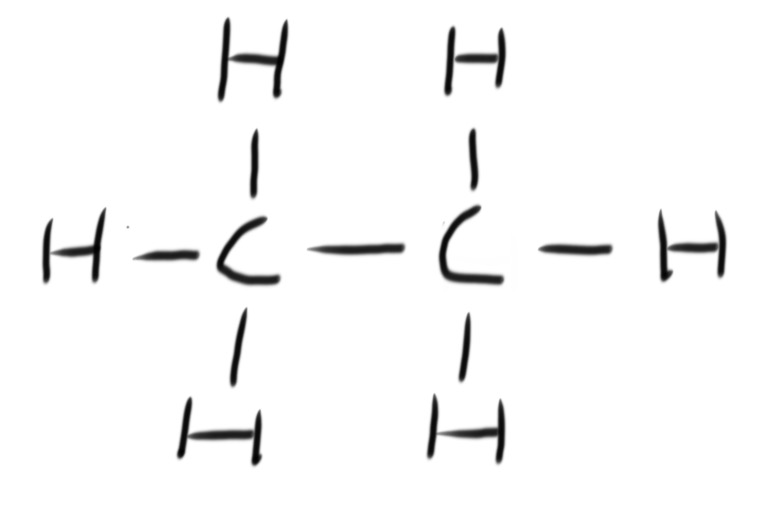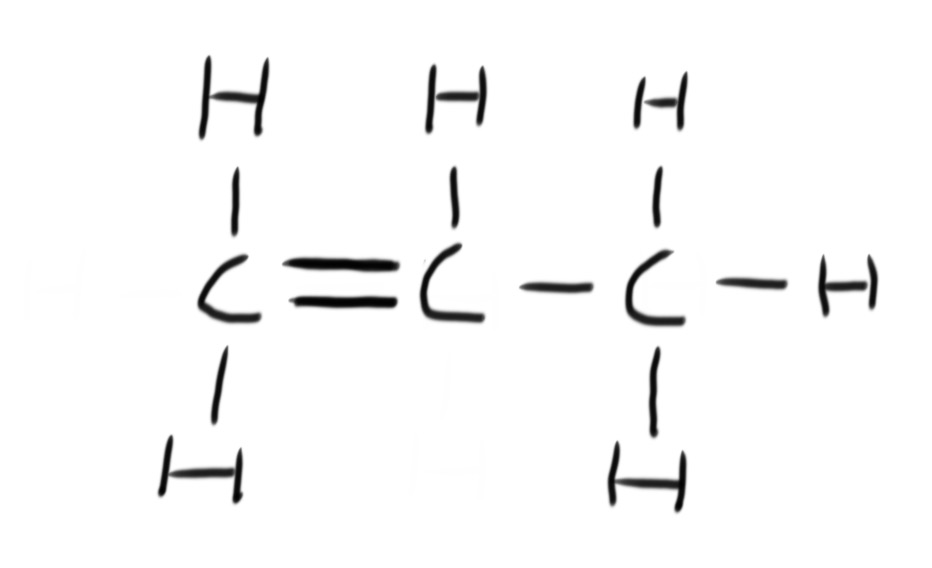A fuel is any compound that has stored energy that can be released when the compound is burned.
Wood, petrol, coal, peat and a number of other fuels have energy-rich chemical bonds created using the energy from the Sun.
Energy is captured in chemical bonds through processes such as photosynthesis and respiration.
Combustion
Combustion is the reaction of burning a compound in oxygen. Hydrocarbons burn in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. This is known as complete combustion.
Combustion Reactions
The experiment below is used to demonstrate the products formed by the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon. The oxygen combines with the carbon to form carbon dioxide and the hydrogen to form water.
hydrocarbon + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
Carbon dioxide gas turns limewater from colourless to cloudy/ chalky. The water produced condenses on the sides of the gas jar. Water turns cobalt chloride paper from blue to pink.
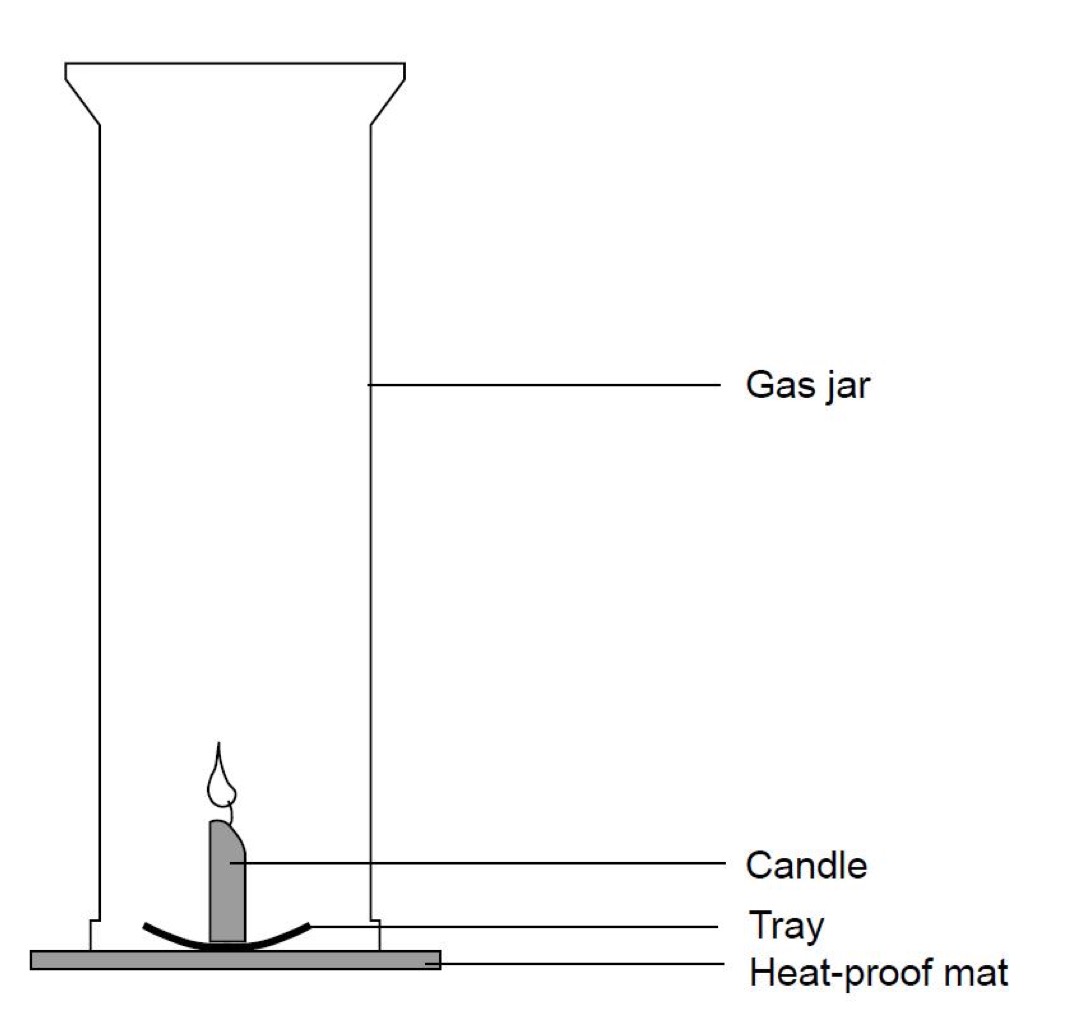
Products of combustion experiment.
Set up the equipment as shown in the diagram below.
Instructions
- Once the equipment has been set up, light the candle and place the gas jar back over the candle.
- When the candle goes out, lift the gas jar up with out tilting and place the lid on the bottom of the jar.
- Test to see if the candle made water by adding a piece of blue cobalt chloride paper, test the sides of the jar. If it turns pink, water is present.
- Repeat steps 1 and 2.
- This time, test to see if carbon dioxide was produced. Pour a little limewater into the gas jar. Swill it around a little. If carbon dioxide is present, the limewater turns cloudy.
Questions
- What is the gas that reacts with the hydrocarbon when it burns?
- What gases does the candle produce when it burns?
- Name another fuel that produces the same gases when it burns.