First, Complete the pretest!!!

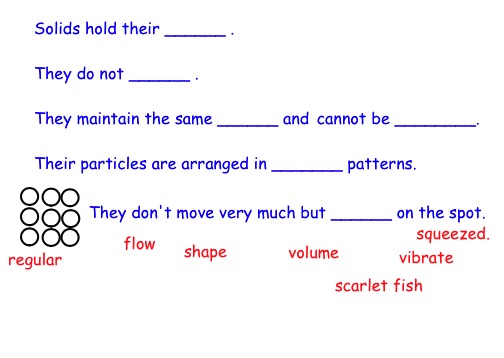
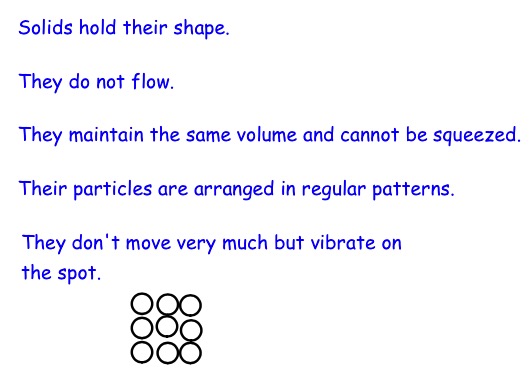
Your teacher will show you the five substances that are in the table below. Decide if they are solids, liquids or gases.
| substance | description |
|---|---|
| Vinegar | |
| Sand | |
| Mercury | |
| Shaving Foam | |
| Corn Flour |
Is custard a solid or a liquid?
Watch the video below. Does it help you to decide?

Look at the range of solids.


Use the simulator below to visulise what particles of solids, liquids and gases look like.
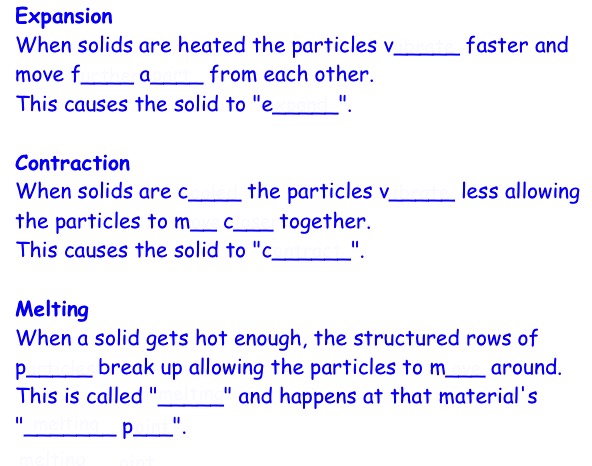
Try to change the solid into a liquid. What happens to the particles?

When solids are mixed together, they mix with the smaller lumps fitting into the gaps between the bigger ones.
They can be easily separated again and there are many machines that have been designed to do this job.

CAUTION: These experiments involve Bunsen burners and VERY HOT metal.
Collect:

Watch the video below to find out what happens to solids and liquids when they are heated.
Watch the video below to find out what happens when solids are cooled then warmed up.
Use the simulator below to find out what happens to particles when they are heated and cooled.
Make sure to click on 'phase changes'.



Look at the range of liquids.
Make a list of the things they have in common.
DO NOT PULL THE SYRINGES APART!
Watch the video below.
What properties do all liquids have in common?

Liquids all flow - but at different rates.
They maintain their volume and are not easily compressed.
They take the shape of their container.

Watch the video below.
In terms of particles, why do some liquids mix but not others?

Alcohol and water mix because the particles of water and alcohol fit in between each other.

Copy the diagram into your notes.
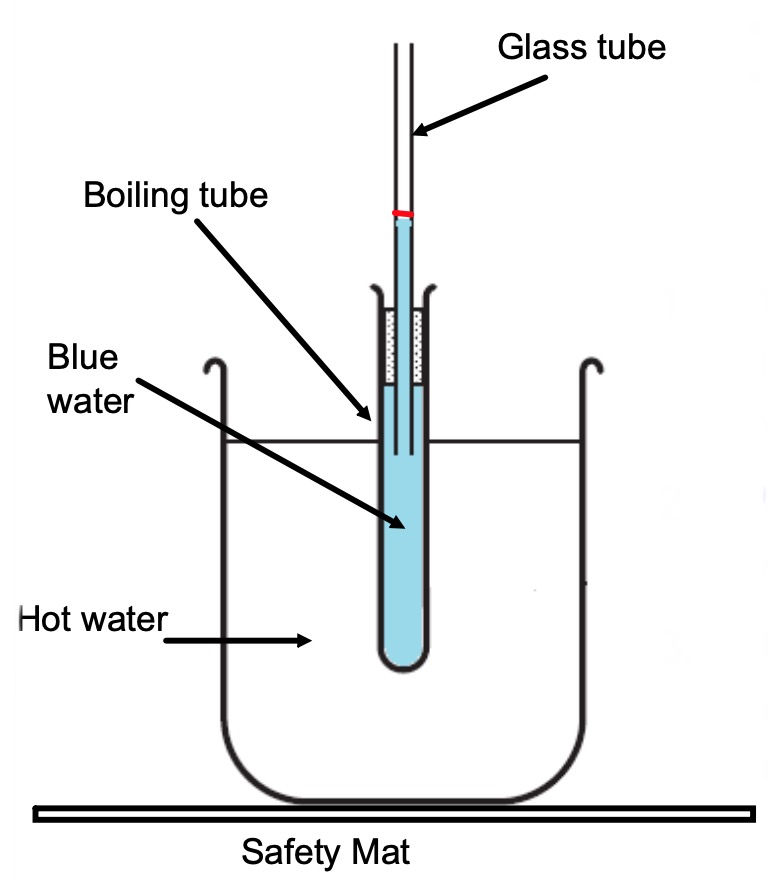
Mark the position of the water in the glass tube at the start, before you have watched the video.
Watch the video of the experiment below.
Add a a line to your diagram to indicate what happened to the liquid.

Open the phase changes simulation. Try to change the particles from solid to liquid to gas and back.

Every liquid can be turned into a s____ or a g__.
When l______ change from a l_____ to a s____ we call it f_______. The particles in the liquid s___ d___ and eventually arrange into s_________ patterns.
The temperature that this happens is called the liquid's "f_______ p____".
When liquids change into a g__we call it b______ or e_________.
E__________ happens on the s______ of the liquid and can happen at l____ temperatures.
e.g. a p_____ evaporating on the pavement caused by the h___ of the sun.
When b______ the particles in a liquid turn into a g__ we call it b______.
The temperature that this happens is called the b______ p____.

Look at the range of containers with gas inside.
On your mini white board, make a list of what all gases have in common.
DO NOT PULL SYRINGES APART
Watch the video on the Noble Gases.
Watch the video on the properties of gases.

Gases e_____ to fill their container.
Gases can be easily squeezed or c_________.
Some gases are l______ than air and others h______.
Gases take the s____ of their container.
Watch the video on diffusion.

When two or more gases meet they mix in with each other sharing the space of the container.
This is called diffusion.
Learning Intention

Your teacher will perform the flask and egg demonstration or you can wathch the video below.
Using your knowledge of particles as much as possible, explain:
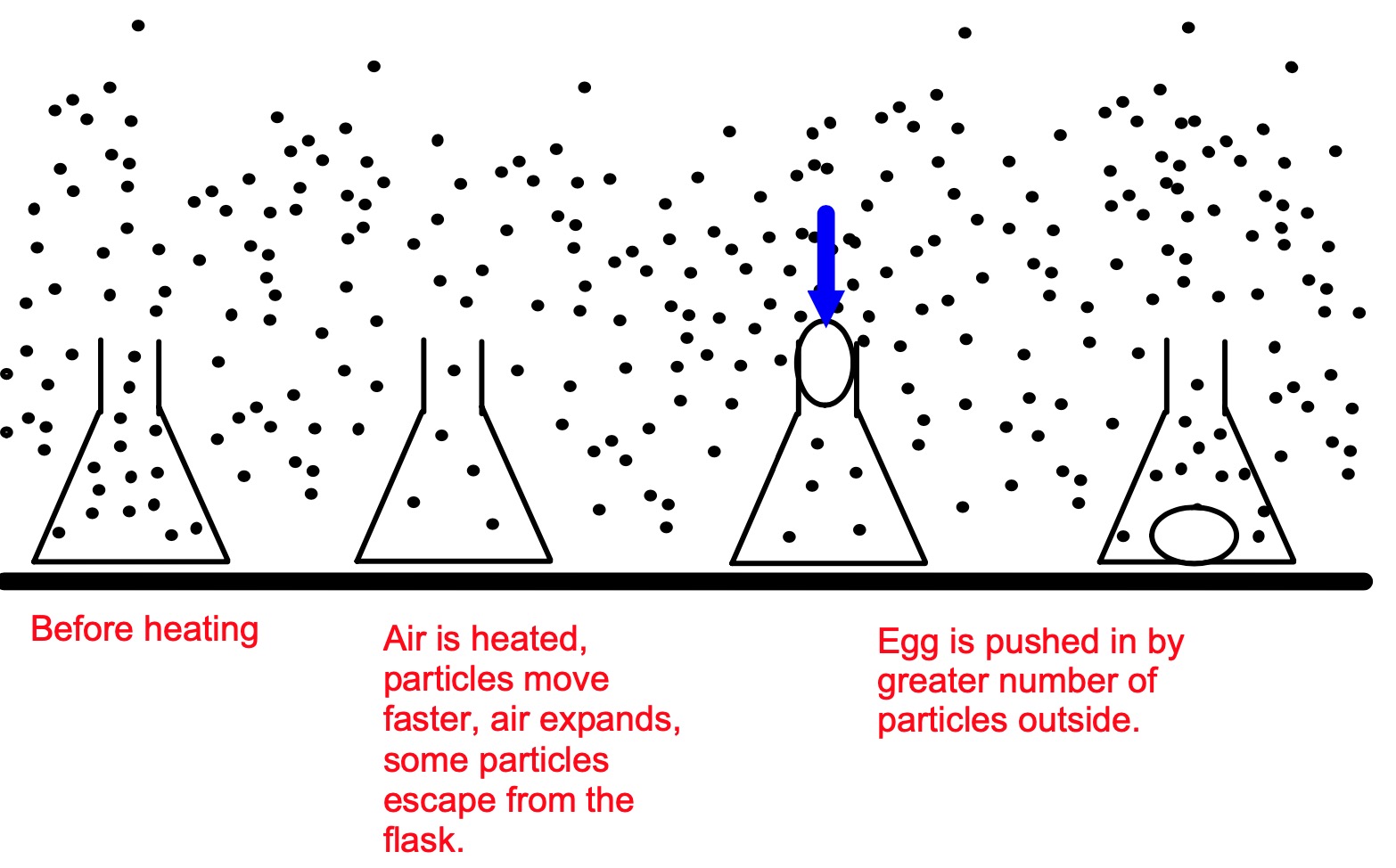

Heating causes the ___ in the flask to ______. Some of the particles ____ ___ of the flask.
There are now fewer particles ______ the flask.
When the egg is placed __ ___of the flask and it is cooled, the air inside _________ and the egg is ______ in by the air particles on the outside.

On a cold morning the windows of your car will steam up. Why is this?
This is called condensation.
Condensation occurs when a gas e.g. water vapour inyour breath, turns into a liquid.
First, Complete the pretest!!!

Soluble - means it will dissolve.
Insoluble - means it wont.
The liquid that things dissolve in is called the SOLVENT.
The solid/liquid that dissolves is called the SOLUTE.
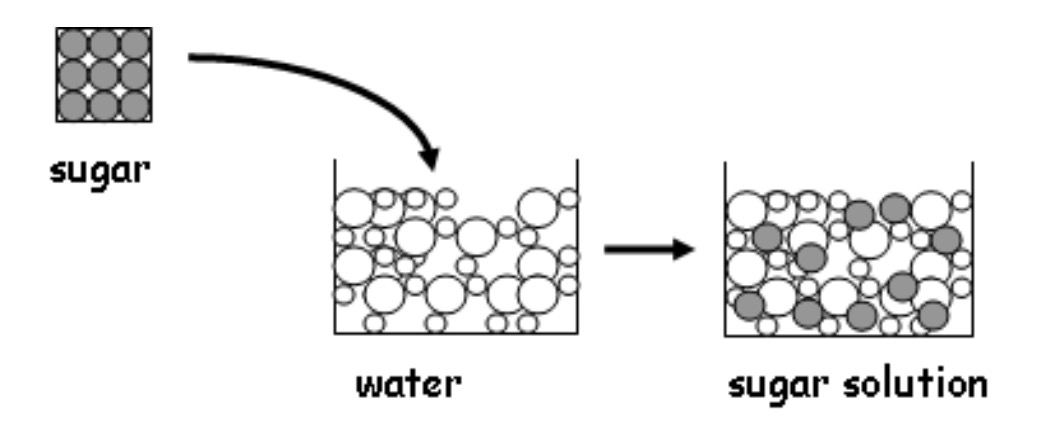
When you put a crystal of a solid e.g. sugar into water it dissolves.
The water separates the sugar particles which were joined in the crystal.
When a solid dissolves in a liquid, the solid is called the solute, the liquid is called the solvent and the mixture is known as the solution.

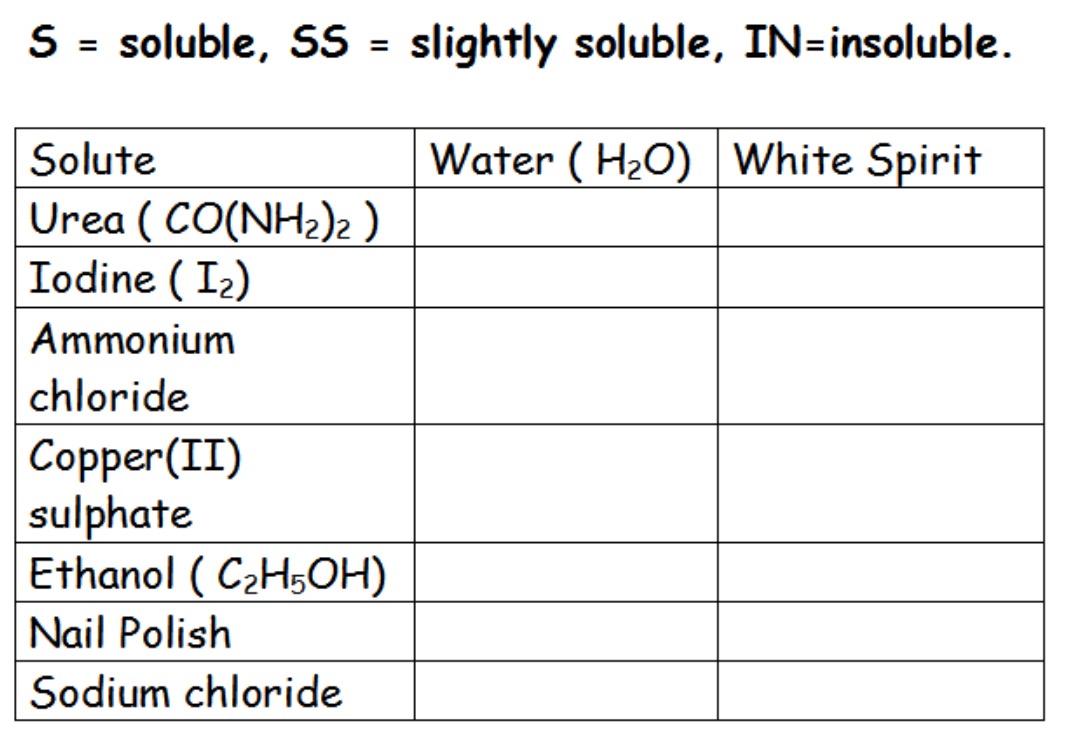
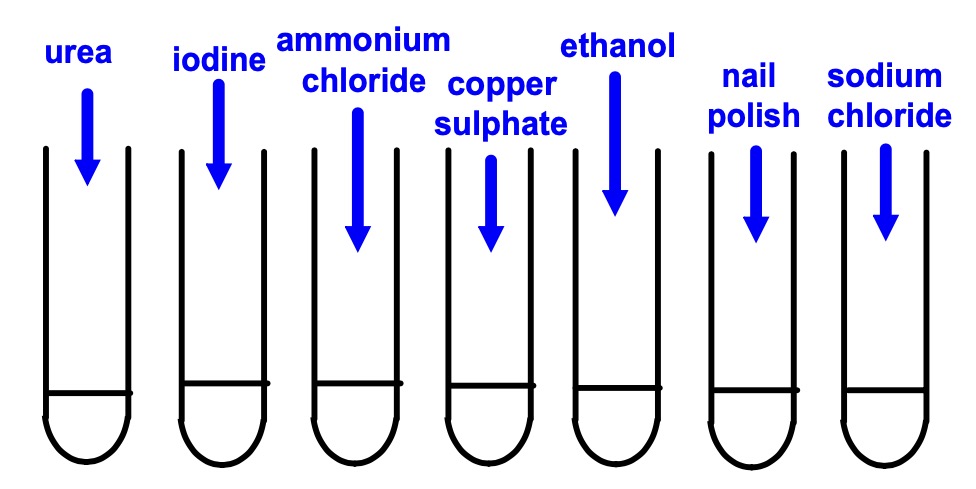
You are going to investigate dissolving 7 solutes in 2 sol
Use the table below to record your results.
Colect:
Instructions

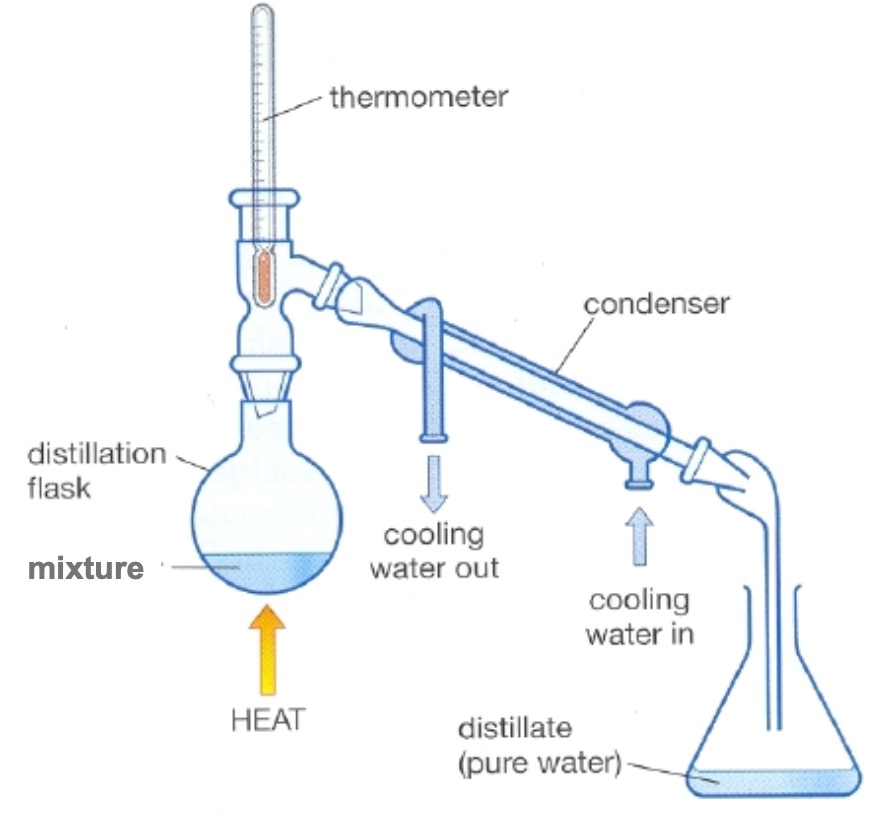
In distillation, the water is evaporated, then the steam (water vapour) is condensed.
Watch the distillation demonstration.
Collect and complete the handout and stick it into your jotter.

Watch the demonstration.
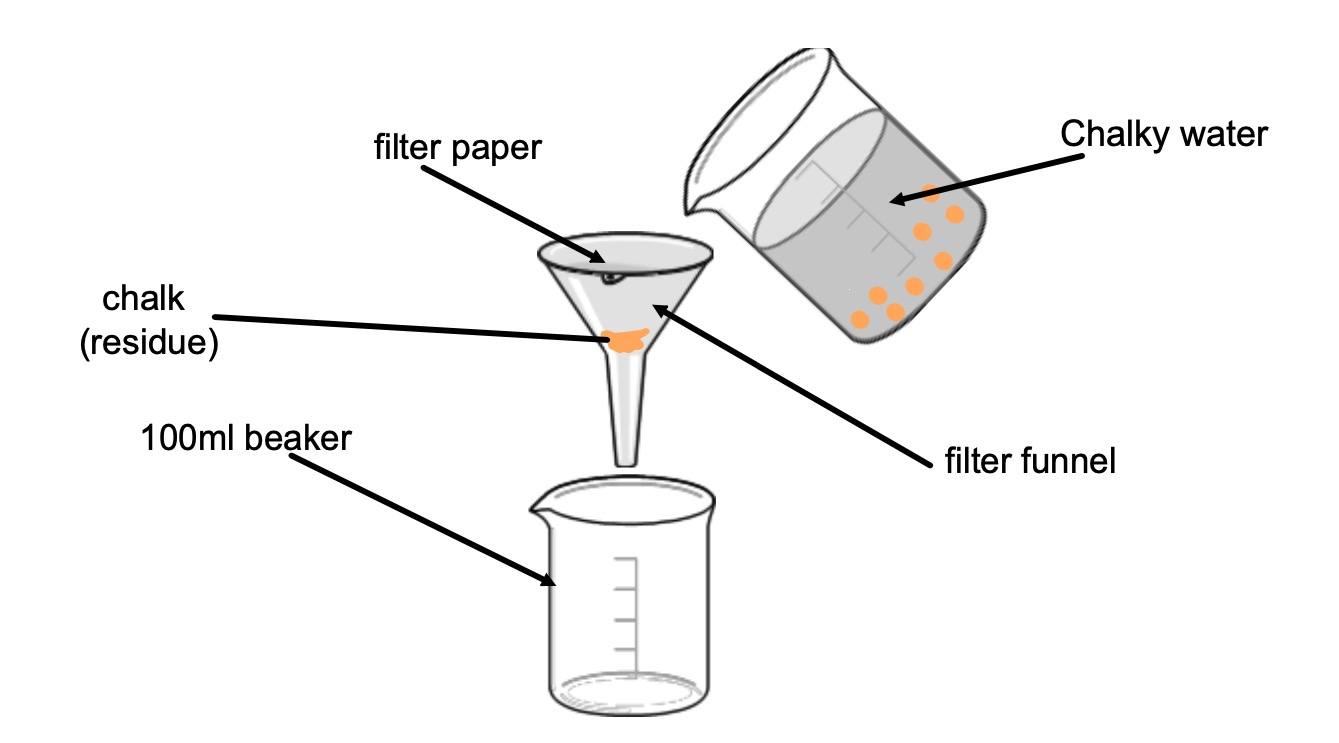
Collect:

The liquid that passes through the filter paper is called the filtrate.
The solid that stays in the filter paper is called the residue.

Collect the following:

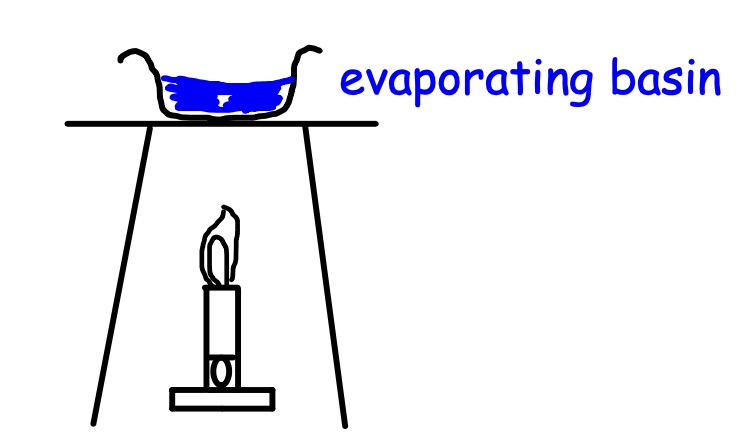
We evaporated the water, it turned into a gas. The blue solute was left behind in the basin.