

In this unit we are going learn more about this DNA, what it's job is and why it is so important.
Watch the video below to find out more.





Animals that are born from parents that are different species (like a mule) are called hybrids. They are infertile.


Can figure out which animals were involved in creating the following hybrids?
______ + Shetland Pony = Zebrony
Grizzly Bear + __________ = Grolar Bear
Cow + _________ = Beefalo
Camel + _____ = Cama
Serval + ______ = Savannah Cat
________ + Goat = Geep
My favourite example of a hybrid is ___________ it is created from a _________ and a __________

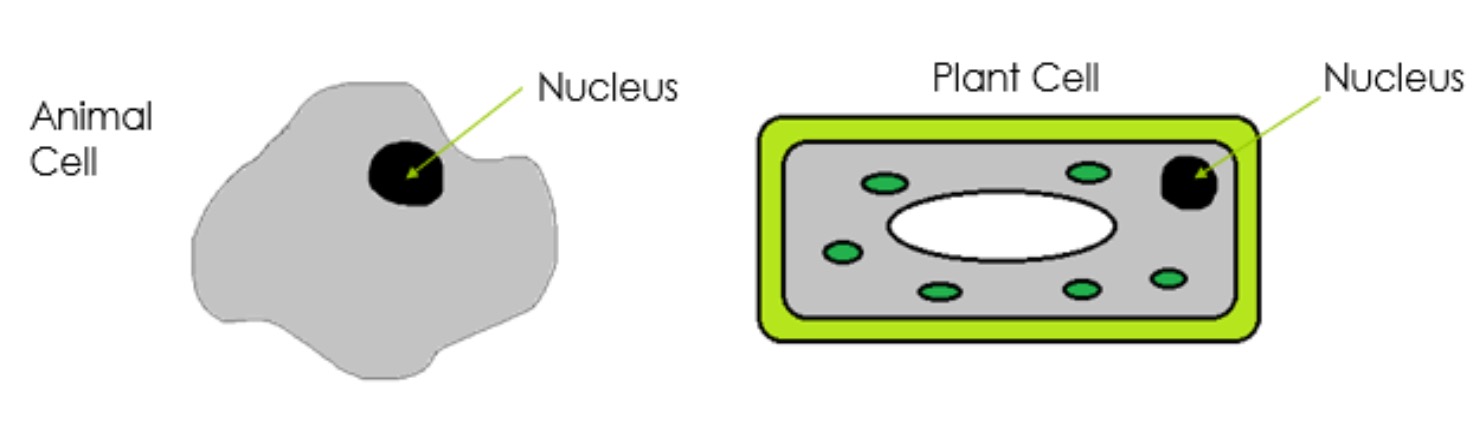
Although members of the same species are very similar to one another they are not identical. This is because variation exists within a species.
Variation is the differences between members of the same species
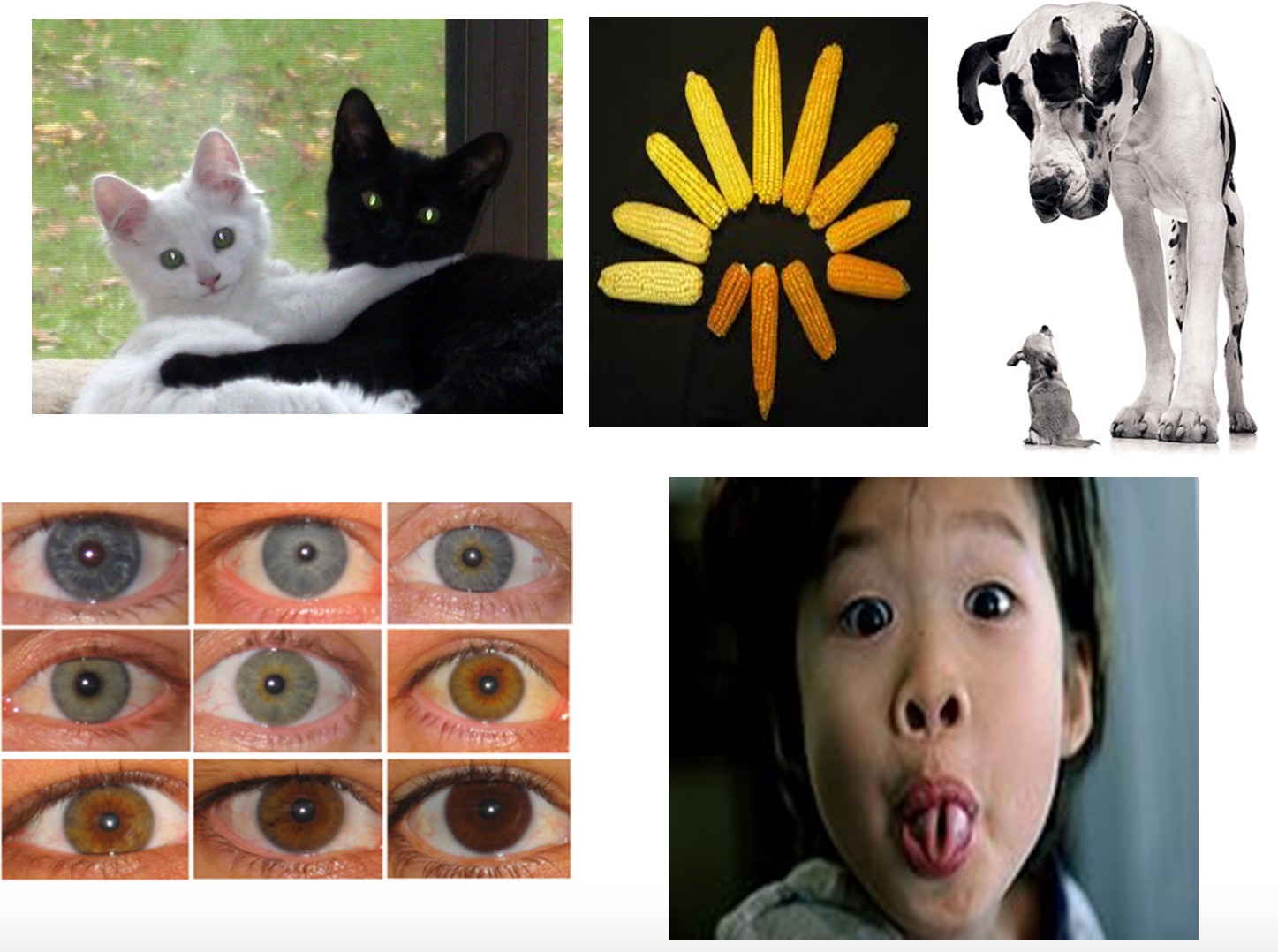

Watch the clip below on variation.
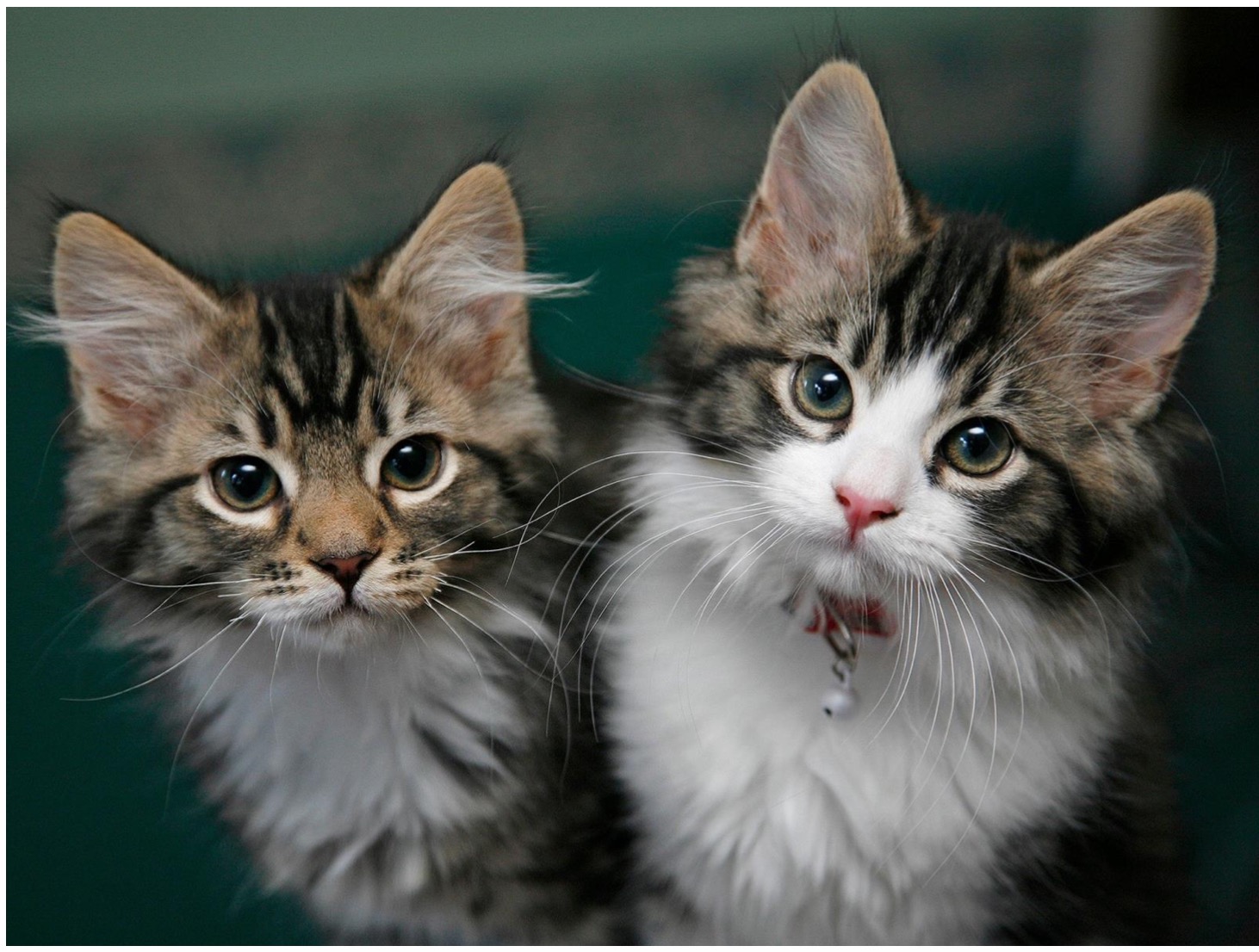

Copy the table below into your notes.
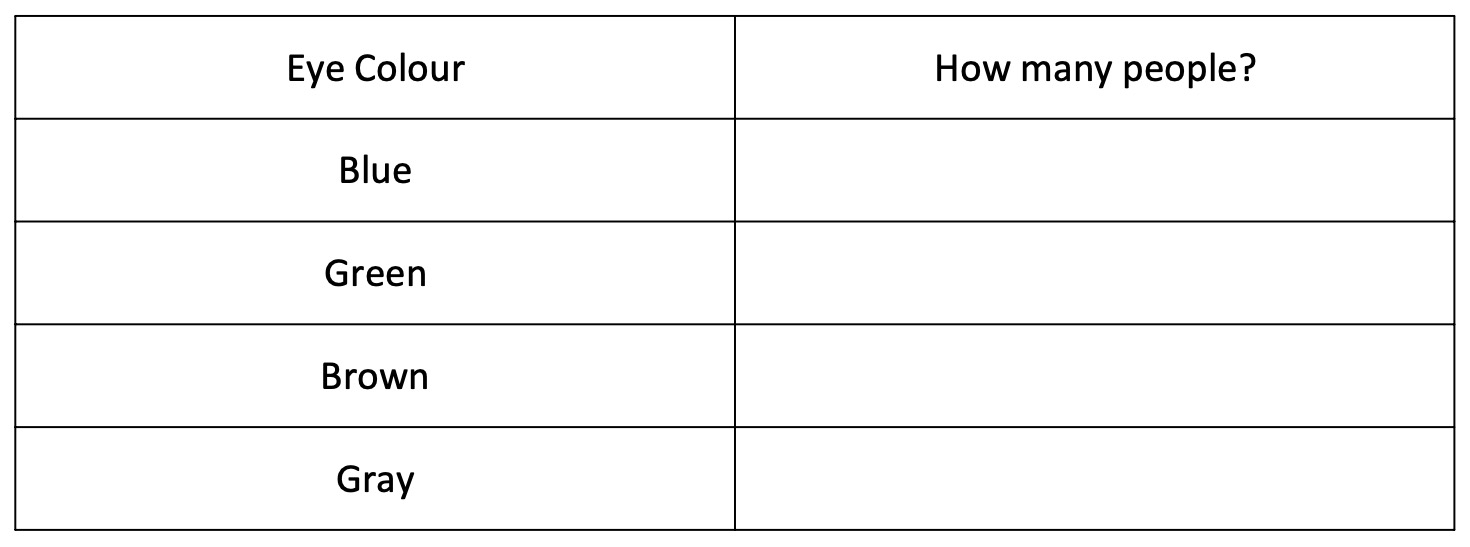
Use your table to record the different eye colours of people in your class.
Copy the table below into your notes.
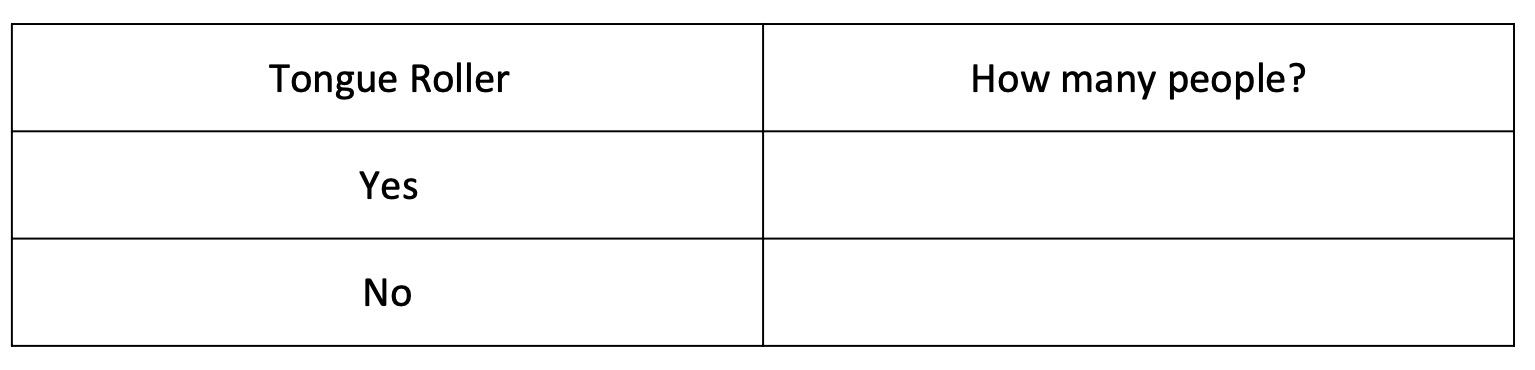
Use your table to record the number of tounge rollers in your class.
Copy the table below into your notes.
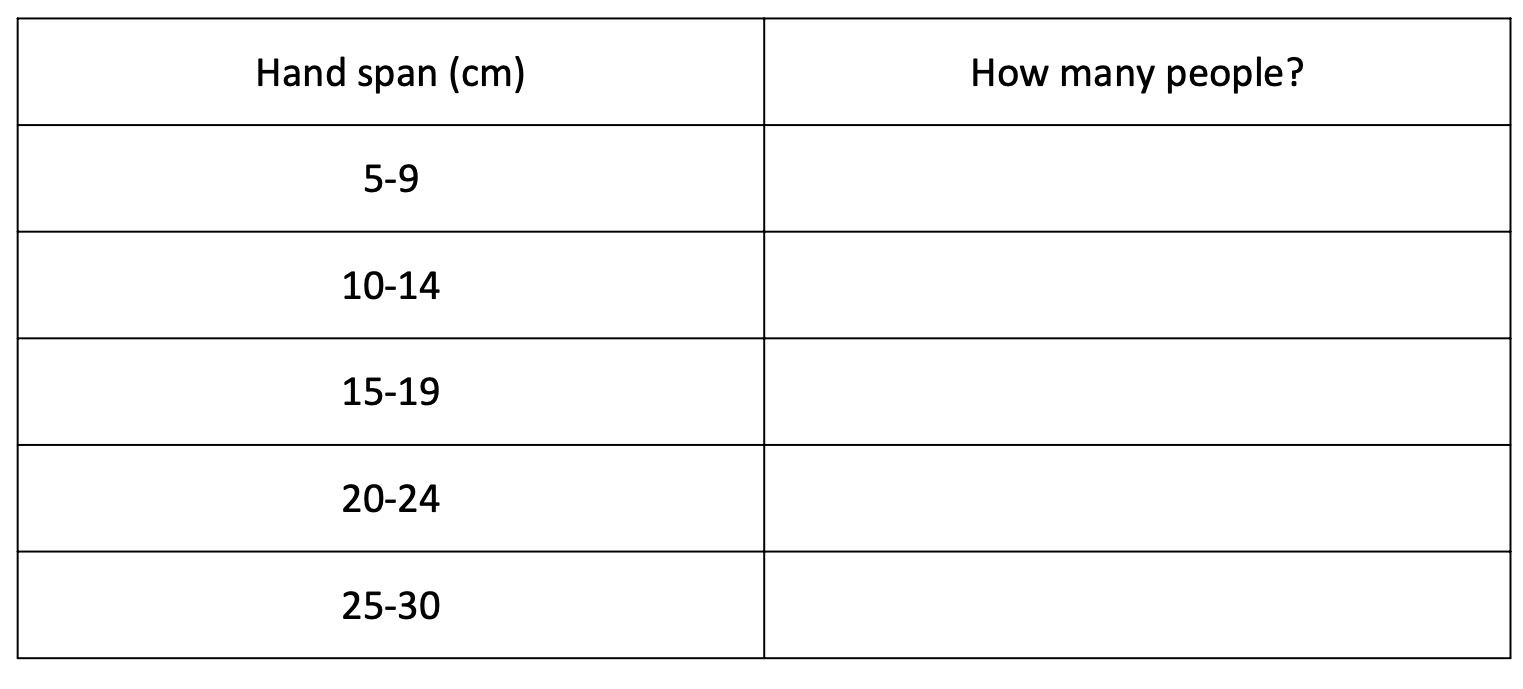
Use it to record the hand span of people in your class.
Draw a bar graph of at least one of your tables.
Draw a line graph of at least one of your tables.




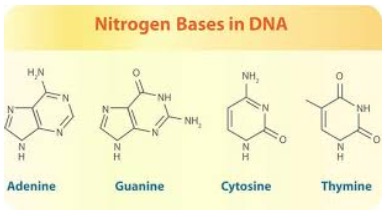
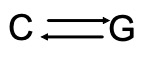
DNA has 4 different bases along the strands

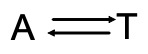
Adenine and Thymine always join together
Cytosine and Guanine always join together

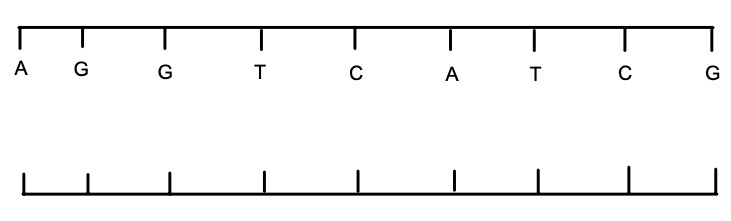
What would be the matching strand for this piece of DNA?
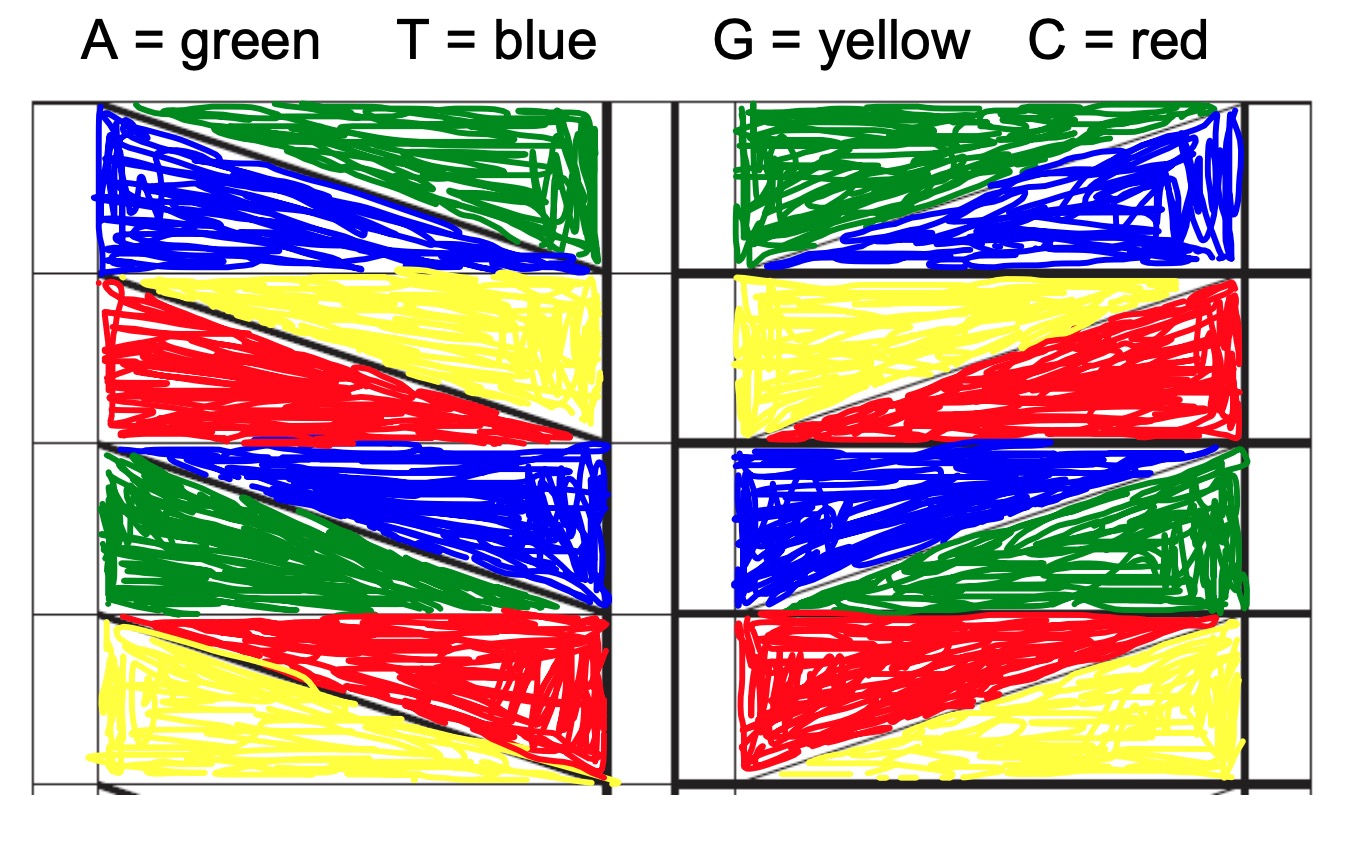
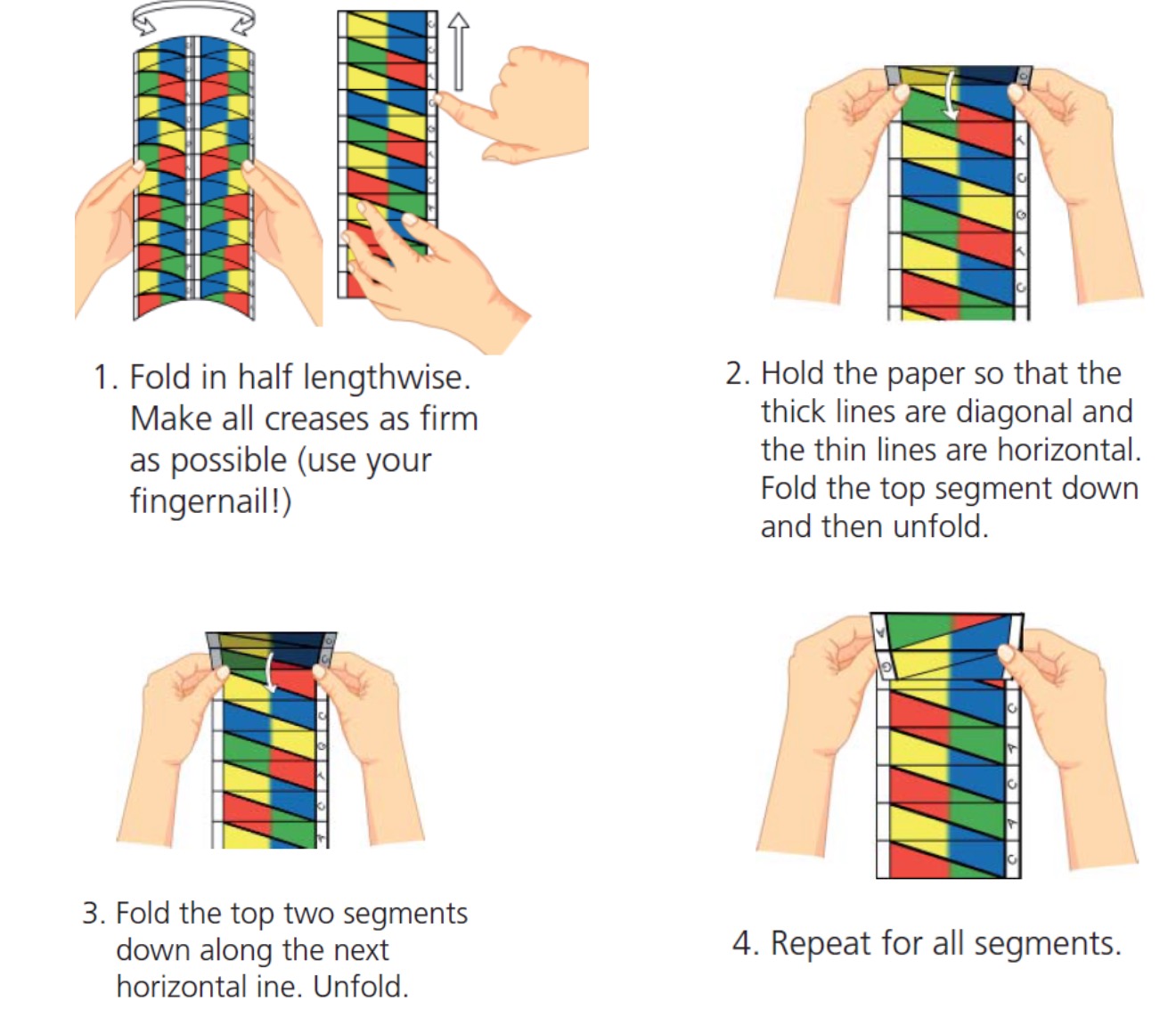
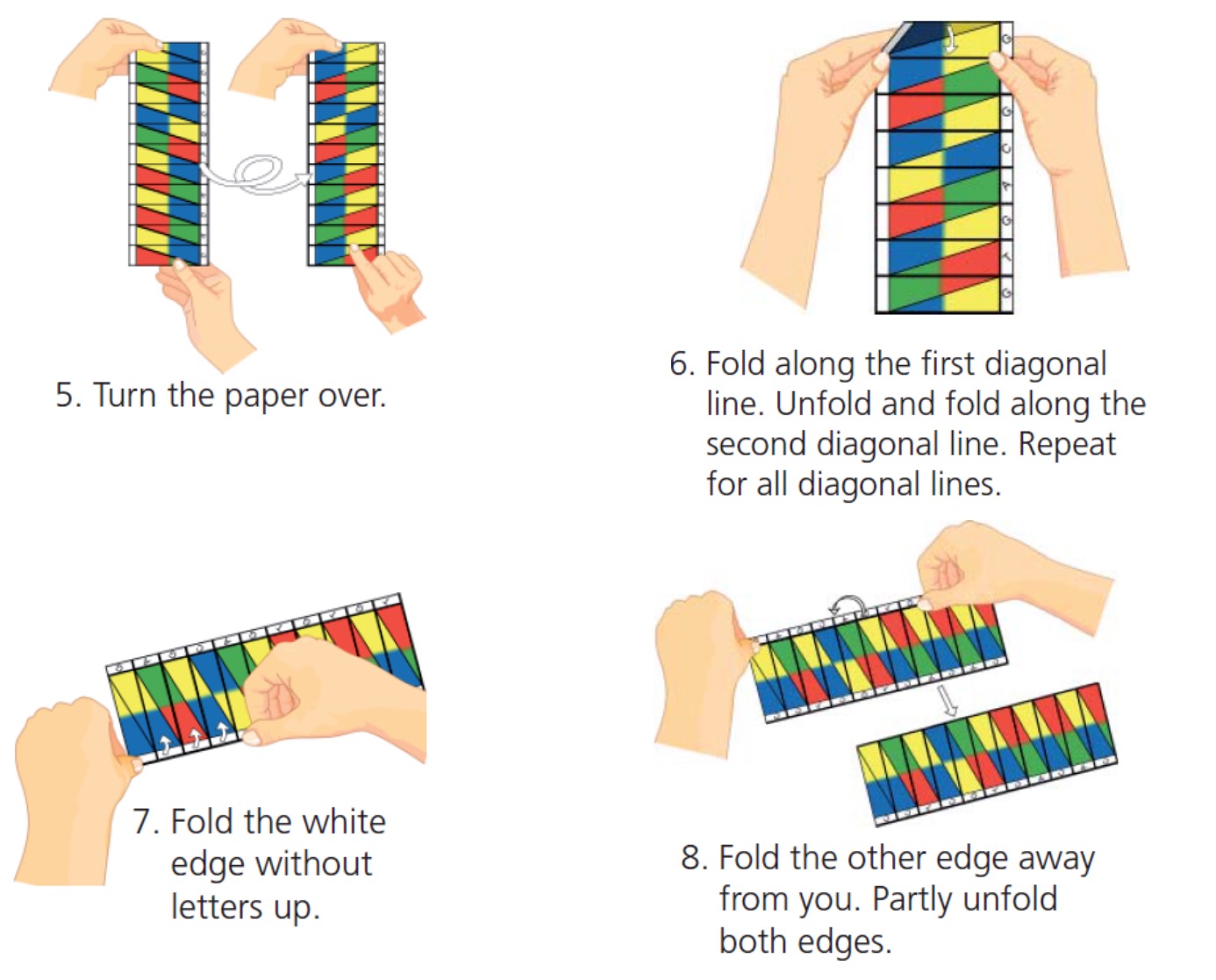
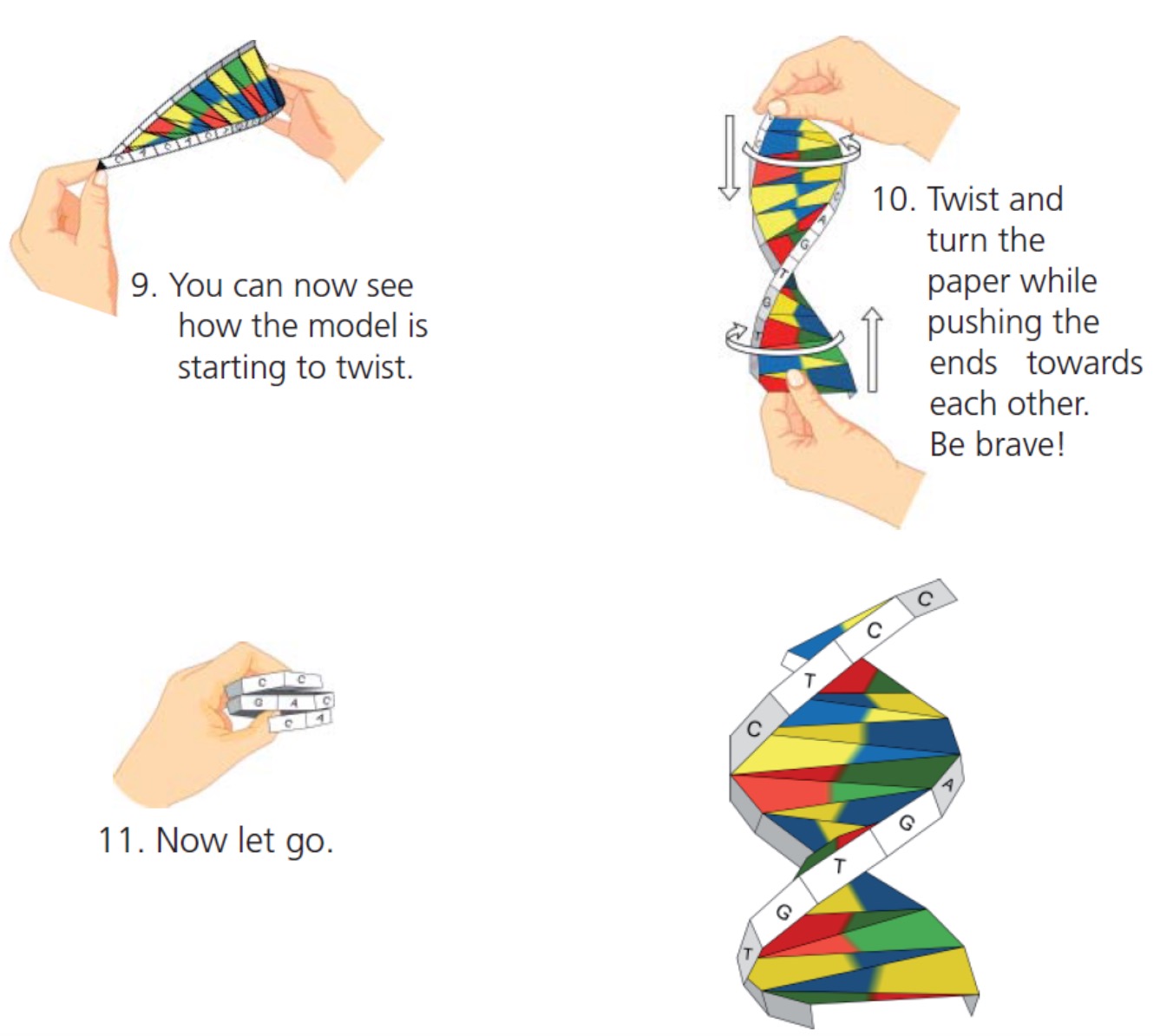
We are going to create origami models of DNA.
To get them to work we have to be careful how we colour it in and how we fold them.
You will need to download and print a template to do this avtivity.
Click on the pdf symbol below to download a template.
Click on the word symbol to download a template.
Note: all folds should have a thin line on the inside and a think line on the outside.
Watch the video below on extracting DNA from strawberries.
Instructions
Watch the video below to recap what you have learned so far about DNA.

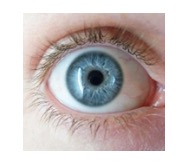
The order of the bases creates a code. This code is used as the instructions to make protein. Although there are only 4 bases, they can make lots of different proteins e.g.
ATTCGGTCATGA codes for blue eyes:
ATTCGCTCATGA codes for green eyes:
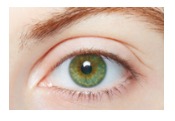
Think about a cake....

The recipe is the instructions that tell you what ingredients to use to make the cake.
In a cell DNA is the instructions for how to make a protein.


Proteins are made from amino acids. The sequence of bases is read by the cell in groups of 3. This tells the cell what amino acids to use to make the protein
You are going to act like the cell and try to read DNA sequences
Each group of 3 bases will represent a particular amino acid
The amino acids match to letters which can then be put together to provide a secret spy note
Can you crack the code and save the world???

We read the code in groups of 3 bases read from the inner circle out.
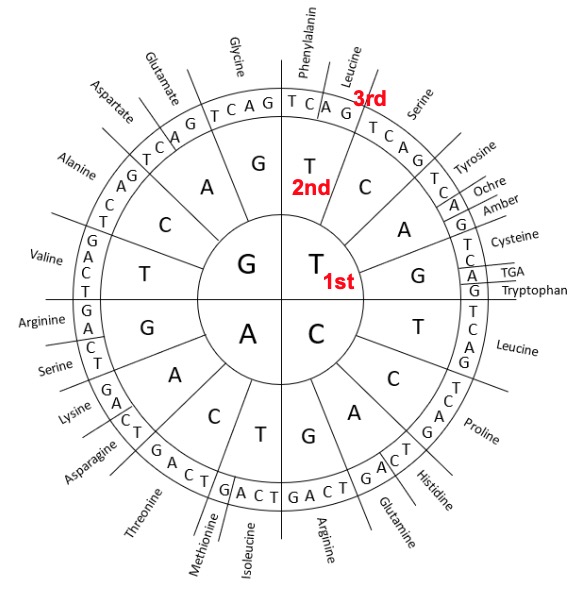
So if we had TTG the amino acid would be leucine.
Now that we know the amino acid we can match it to a letter
Leucine would be an L
What would be the amino acid and letter for the following?

Greetings, Agent
Intelligence sources have revealed to us that the terrorist organisation CLONE (Conspiracy to Liberate Obnoxious and Nasty Enemies) is preparing to threaten the free World with a terrible and secret plot. Our agents have intercepted several messages from CLONE which we believe may contain information about this dreaded plot. Unfortunately, all of the messages are written in the insidious GENETIC CODE.
Your mission is to translate the codes, using the code key provided. Fill in the correct single-Letter abbreviation for the amino acid that is coded by each triplet. Good Luck!

Watch the video below on how DNA fingerprinting is used.

DNA profiling/DNA fingerprinting has many uses


DNA can be used to help with investigations to identify and eliminate suspects:
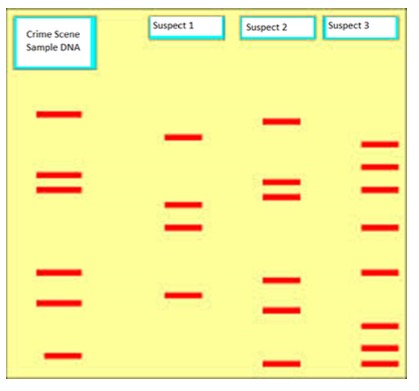


DNA can be used to find out who the biological father of a child is:


DNA can be used to work out if someone has inherited a genetic disease:

DNA can be used to identify the source of meat in supermarket ready meals:

Think about the following:


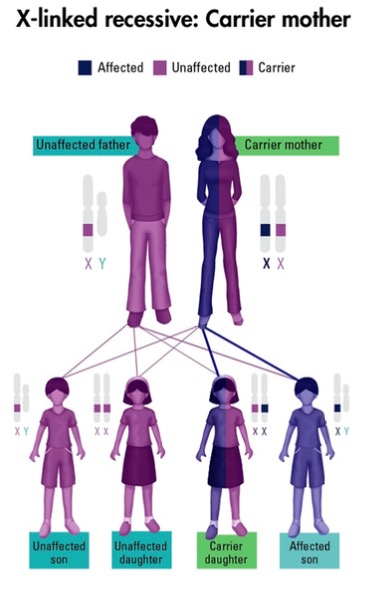
Reproduction is the production of new members of a species.
For a species to survive, it must produce enough young to replace those that die.
Sexual reproduction needs two parents. Each parent has to produce special sex cells, which are made in the sex organs (reproductive system).

Watch the video below on the male and female sex cells.

Animals have specialist cells for reproduction.
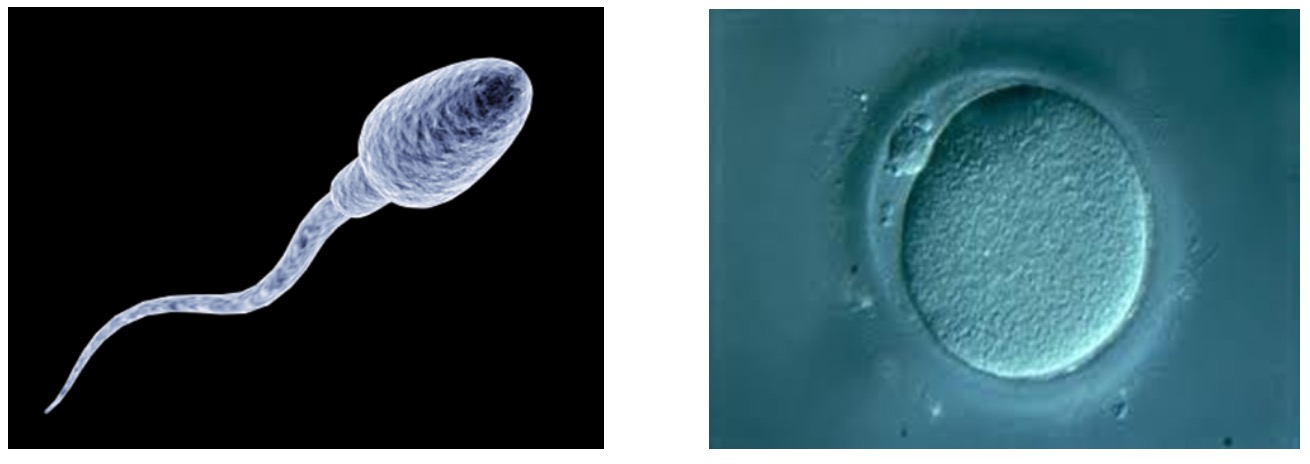

Copy the diagram into your notes.
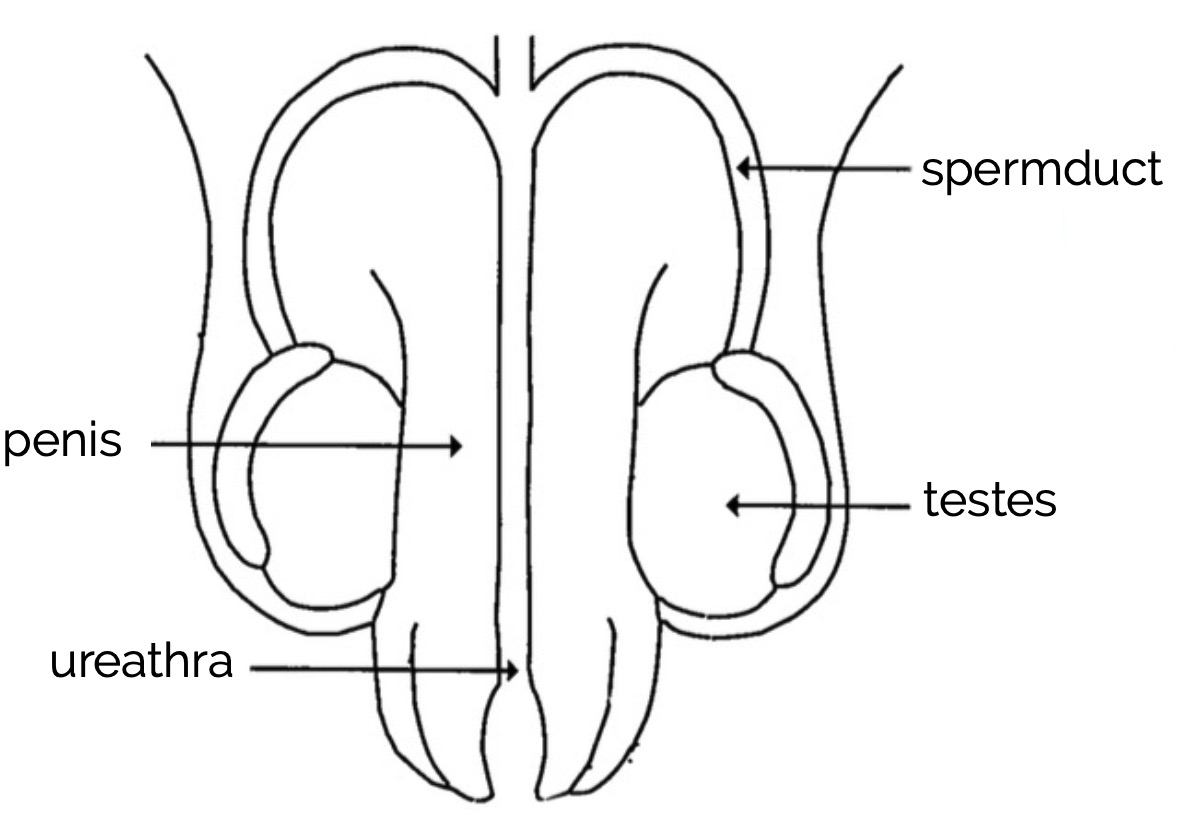
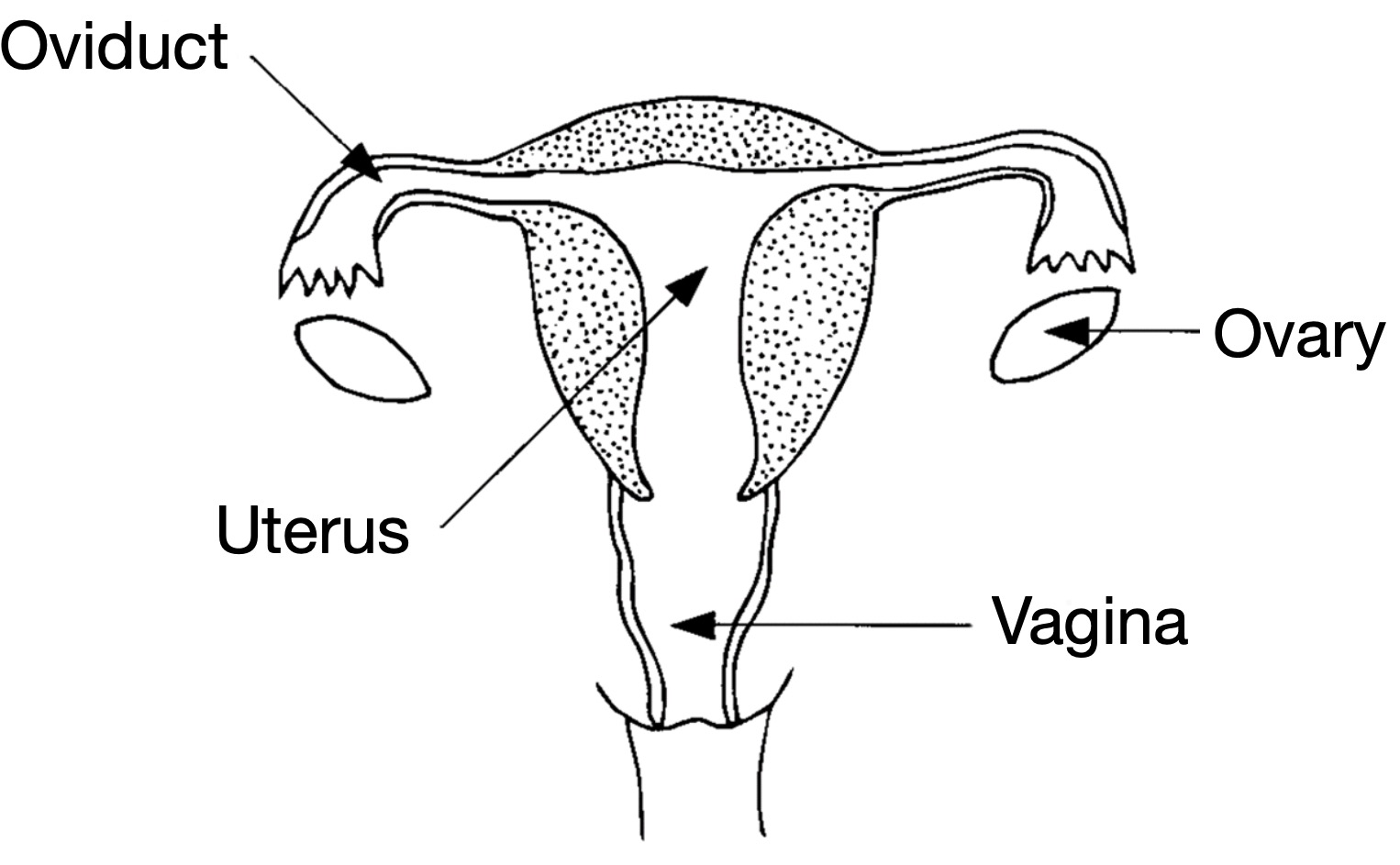
Copy the diagram below into your notes.
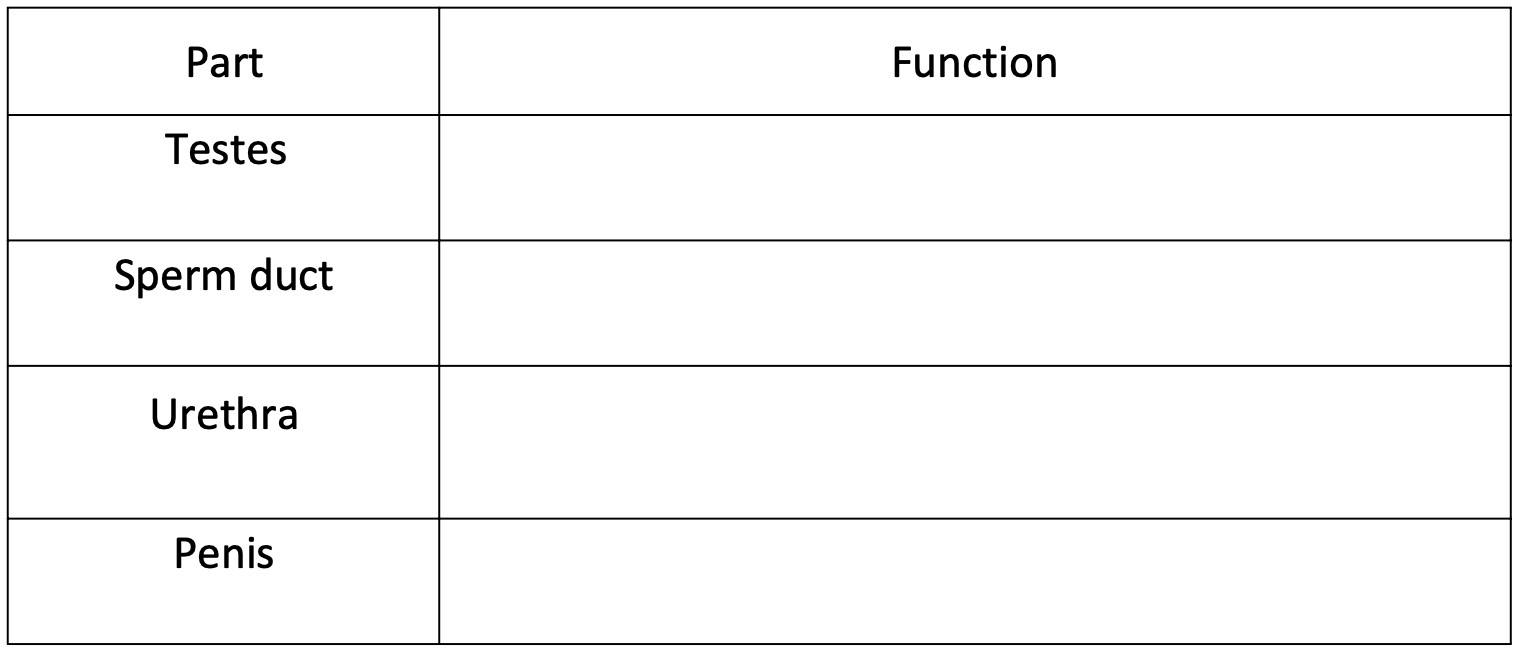
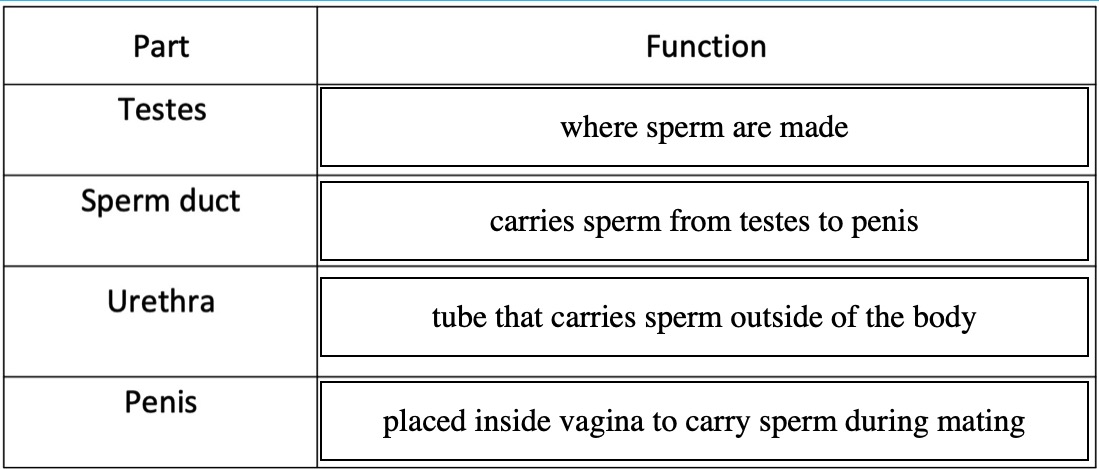
Complete the following table and stick it into your notes.


After intercourse sperm are released into the vagina and their epic journey begins. Click on the picture to see this journey.

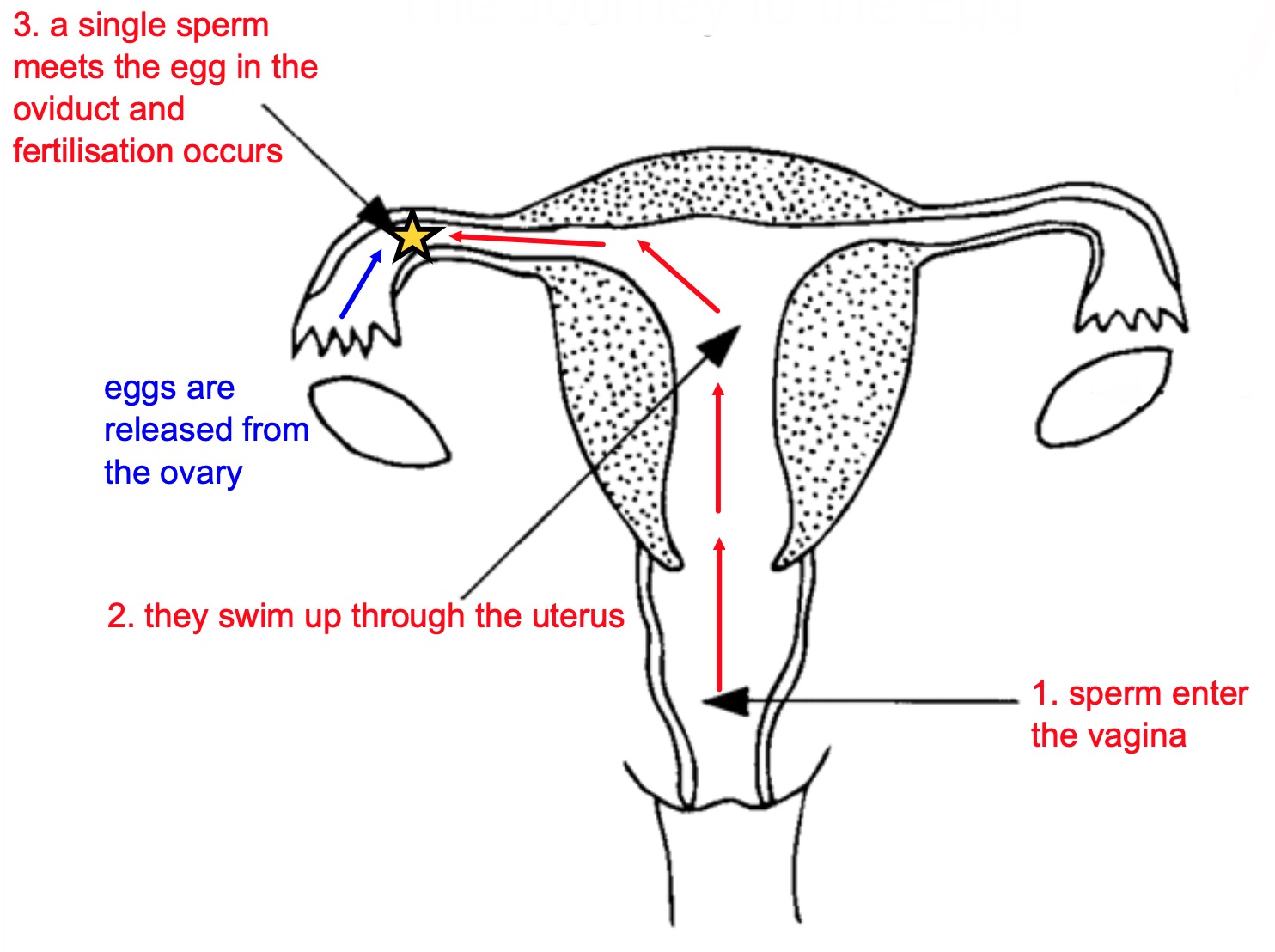
Fertilisation occurs when the nucleus from the sperm joins with the nucleus of the egg.
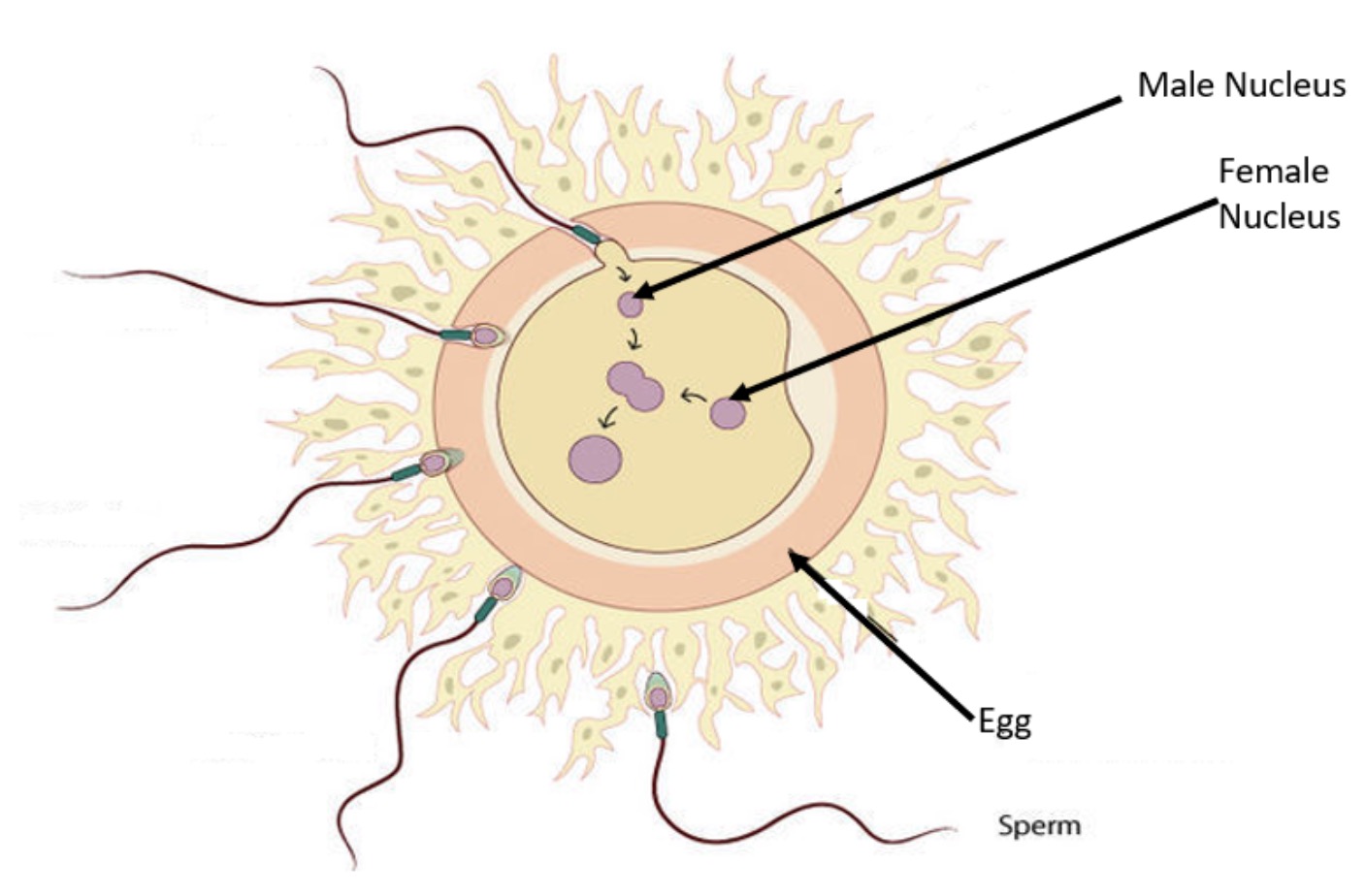

When the head of one sperm gets into the egg, the male nucleus fuses with the female nucleus. This is fertilisation.
The fertilised egg now has a complete set of DNA. 23 chromosomes from the male and 23 chromosomes from the female.
The newly fertilised egg is now known as an embryo.
Watch the video below to see this process.
 In humans pregnancy lasts approximately 40 weeks.
In this time the embryo that started out as a single cell will develop all the characteristics that make us human.
The average weight at birth 7.7lbs (3.5kg).
Pregnancy is split into 3 stages called trimesters each lasting approximately 3 months.
In humans pregnancy lasts approximately 40 weeks.
In this time the embryo that started out as a single cell will develop all the characteristics that make us human.
The average weight at birth 7.7lbs (3.5kg).
Pregnancy is split into 3 stages called trimesters each lasting approximately 3 months.
Watch the video below on the first trimester.
Watch the video below on the second trimester.
Watch the video below in the third trimester
Label the diagram using the words below.
Foetus
Placenta
Umbilical Cord
Amniotic Sac


Pregnancy in humans lasts 40 weeks. While in the uterus the p_______ provides the foetus with food and oxygen from the mother and takes away waste materials.
