Lesson 1 - Making, Testing and Using Hydrogen
Learning Intentions
- To know the properties of hydrogen.
- To know the chemical test for hydrogen.

Starter
What do you know about hydrogen?

Notes - Hydrogen
Hydrogen is an element.
This means that hydrogen is made up of atoms of one kind only.
The chemical symbol for hydrogen is H.
At room temperature hydrogen is a gas.

Activity - Making and Testing Hydrogen
- Write and underline the title, 'Making and testing hydrogen'.
- Collect a copy of the diagram below and stick it into your jotter.
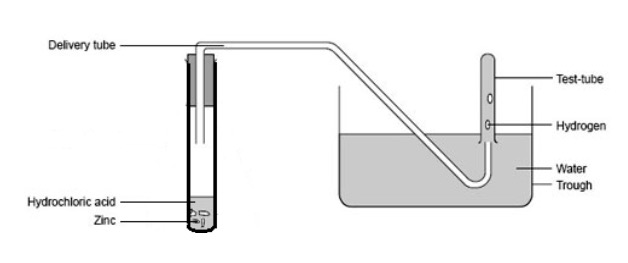
- Copy table below into your jotter under and give it the heading 'Results'
| Test Tube |
Observation |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
- Collect the equipment in the list below.
- safety mat and goggles
- test tube rack
- one boiling tube
- 3 test tubes
- 3 stoppers
- a plastic tub
- delivery tube
- bottle of 1M hydrochloric acid
- Follow your teacher's instructions for the experiment.

Results

Notes - Properties of Hydrogen
Lesson 2 - The Properties of Hydrogen
Learning Intention
- To know the properties of hydrogen.

Notes - Planning an experiment
Before scientists do an experiment they make a hypothesis.
They write down what they think their experiment will show them and why they think that.

Activity 1 - Is hydrogen more dense or less dense than air?
Collect a copy of the worksheet in the picture below.
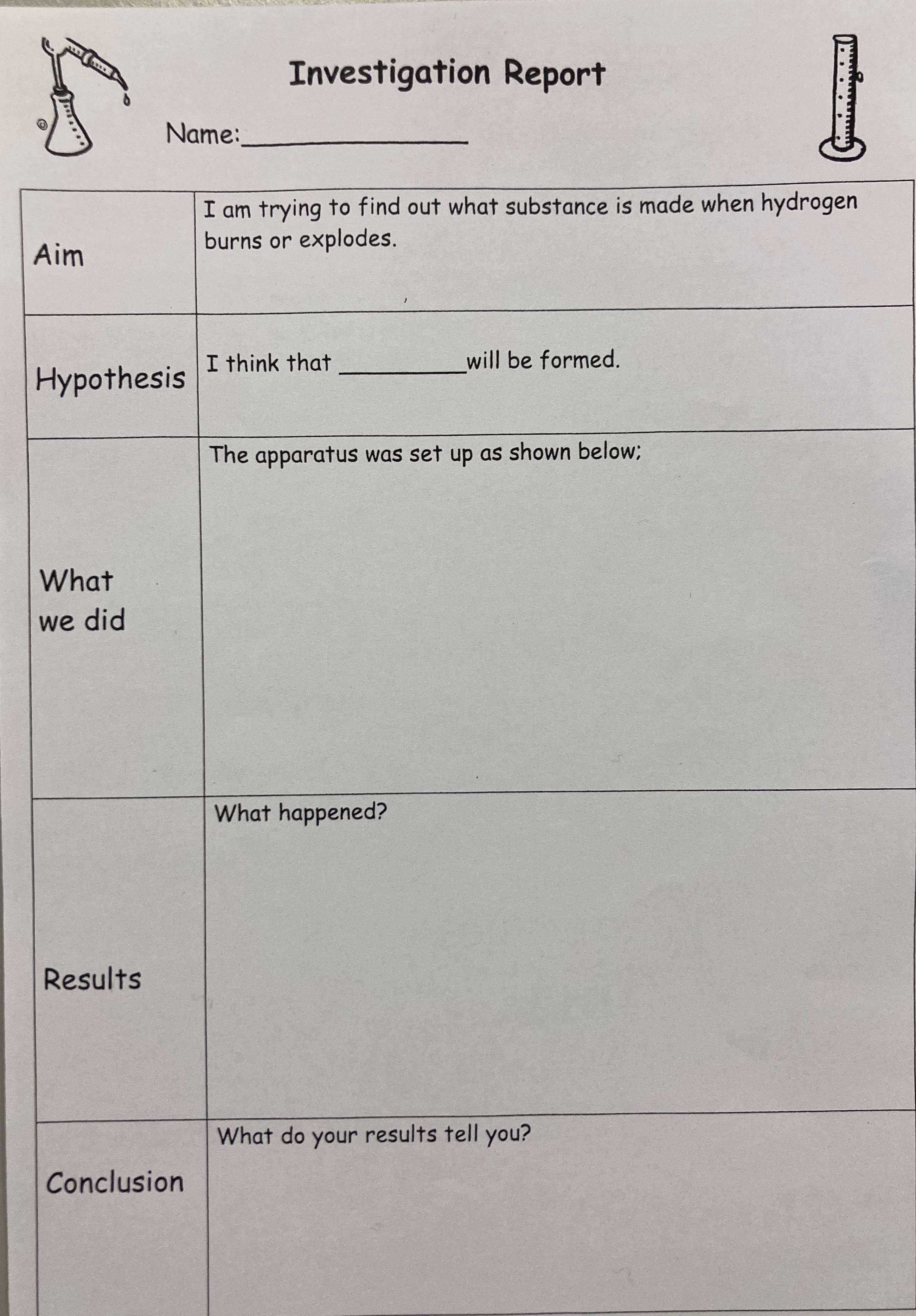
Write down what you think (hypothesize) will be formed when hydrogen burns in air.
Collect the following equipment:
- safety mat and goggles
- Bunsen burner
- Wooden splint
Do the following or as instructed by your teacher:
- Put on safety goggles
- Test Tube 1
- Hold the test tube upside down
- Take off the stopper.
- Wait 30 seconds keeping the test tube upside down.
- Test with a burning splint. Is any hydrogen left in the test tube?
- Repeat with Test Tube 2, this time holding it the right way up for thirty seconds. Is there any hydrogen left this time?

Results - density of hydrogen
Draw a labelled diagram of the two test tubes.
Copy and complete:
Hydrogen gas is more/less dense than air.

Activity 2 - What happens when water is added to cobalt chloride paper?
Write down what you think (hypothesize) will happen to the cobalt chloride paper and why.
Do the following:
- Put on safety goggles
- Collect a small beaker of water.
- Get one piece of dry cobalt chloride paper.
- Get a dropper.
- Drop two drops of water onto the cobalt chloride paper.

Results - Adding water to cobalt chloride paper
Copy and Complete:
Cobalt chloride paper is b___ when dry and p___ when wet.

Activity 3 - What new substance is made when hydrogen burns?
Write down what you think (hypothesize) will happen when hydrogen is burnt and why.
Do the following:
- Make or collect a test tube of hydrogen.
- Take off the stopper.
- Use a lighted splint to do the 'pop test'.
- Put a piece of dry cobalt chloride paper to the test tube and re-stopper it.
- Wait.
Results - Burning Hydrogen
Copy and Complete:
When h_______ burns or explodes, it combines with o_____ from the air to form w____.
The chemical name for water is hydrogen oxide.
The word equation for the reaction is:
hydrogen + oxygen → water
The chemical formula for water is H2O.
Lesson 3 - Making Hydrogen from water
Learning Intentions
- To explain how hydrogen can be made from water.

Activity - What happens when an electric current is passed through water?
Glue a picture of the Hoffman voltameter into your jotter, and copy this table:
| Electrode |
Gas made |
Test Used |
| Negative Electrode |
|
|
| Positive Electrode |
|
|
What happened when your teacher switched the electricity on?
Do the following:
- Complete the table
- Collect a copy of Chemical Science 3. Read pages 28-30. Answer questions 1-3 in your jotter.
- Collect Starting Science 2. Read pages 16 and 17, and answer the questions on each.
Lesson 4 - Metals and Water
Learning Intentions
- I know that the metals in group 1 are called the alkali metals.
- To know what will happen when a metal is added to water.

Notes - Metals reacting with water
Certain metals when they react with water are also capable of producing hydrogen from water.

Activity - Alkali Metals Reacting With water
Watch your teacher demonstrate the alkali metals reacting with water.
The video below shows the bigger pieces of alkali metals reacting with water as well as some that can't be done in school.

Activity - Other Metals that React with Water
Copy the table below into your notes:
| Metal |
Reaction with Water |
Test for Hydrogen |
| magnesium |
|
|
| iron |
|
|
| calcium |
|
|
Collect the following equipment:
- safety mat and goggles
- test tube rack
- bunsen burner
- 3 test tubes
- spatula
- a wooden splint
Watch your teacher demonstrate this experiment then follow the instruction below:
- About 2cm of water in each test tube.
- Add magnesium to your first test tube.
- Test to see if hydrogen gas is produced.
- What did you see?
- Write this down in your results table.
- Do steps 1-5 again with calcium then with iron.
Results
Do the following:
- Method: Draw a labeled diagram of your experiment and equipment.
- Conclusion: copy and complete the conclusion below:
The metal that reacts most with water is c______.
The metal that reacts least with water is i___.
Some metals react with water to make h_______ gas.
Lesson 5 - Metals and Acids
Learning Intentions
- To know what will happen when a metal reacts with an acid.
- To know the order of reactivity of magnesium, aluminium, zinc, iron, and tin when they react with acid.

Activity - Reaction of Metals with Acids
Copy the table below:
| metal |
observation |
| magnesium |
|
| iron |
|
| tin |
|
| zinc |
|
| copper |
|
| aluminium |
|
Collect the equipment below:
- Safety mat & goggles
- Test tube rack
- 6 x Test tubes
- Spatula
- Heat mat
- Bunsen burner
- Splint
Watch your teacher demonstrate the experiment then follow the instructions below:
- Collect a bottle of acid.
- Add about 2cm of acid to each test tube.
- Add one bit of magnesium to your first test tube.
- Test to see if hydrogen has been given off.
- Write what you see in your results table.
- Repeat for the remaining metals.

Notes - Metals and Acids
To solve the anagram put the first letter of the metal's name in order of reactivity.

Lesson 6 - Making an Indicators
Learning Intention
- An indicator is a special dye which changes colour in acids and alkalis.
- Many foods include dyes which act as indicators, e.g. red cabbage, beetroot, red onion.
Red Cabbage Indicator
Click on the image below to watch the video below on making red cabbage indicator.
Extension
Use the information from the video to write a set of instructions for making red cabbage indicator.

Activity - Making an Indication
Copy this diagram, and label it using the words:
Tripod Stand 100cm3 Beaker Red Cabbage Water

Copy the table below into your jotter.
| substance |
colour change |
| water |
no change |
| acid |
purple → ___ |
| alkali |
purple → _____ |
Collect the following items:
- safety mat and glasses
- 100cm3 Beaker
- tripod stand
- Bunsen Burner
- Red cabbage
Watch your teacher demonstrate how to carry out this experiment then:
- Cover the red cabbage with 50cm3 of water.
- Boil the Red Cabbage for 4 minutes.
Results
Answer the following questions in sentences in your jotter.
- What vegetable did you use to make the indicator?
- What colour was the indicator you made?
- What colour did your indicator turn in acid?
- What colour does your indicator turn in alkali?
- A mystery solution turns your indicator red. Was it an acid or and alkali?
- Can you explain your answer?

Notes - Indicators
Copy and complete the notes below into your jotter.
An indicator is a dye that changes colour in different conditions.
Fruits and vegetables can be used to make indicators.
In class we used R__ C______ to make an indicator.
The colour changes I noticed were:
Acid P_____ → R__
Alkali P_____ → G____
Extension - Other indicators
Turmeric as an indicator.
Bicarbonate Soda as an indicator.
Lesson 7 - Investigating the pH Scale
Learning Intentions
- Universal indicator is a mixture of dyes which change colour depending on the pH of the solution.
- Use universal indicator to group household materials into acid and alkali.
- pH paper is paper which has been soaked in universal indicator.
Notes - Universal Indicator
Universal indictor is a special dye that when added to a solution (liquid) is:
Red-orange in acid
green in neutral solutions
blue - purple in alkali
Activity - Testing pH of Household Substances
Copy the table below into your notes. You will need space for nine rows.
| Name of substance |
Colour of Universal Indicator |
pH number |
Acid, alkali or neutral |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equipment
Collect the following equipment:
- safety mat & glasses
- dimple tile
- bottle of universal indicator and colour chart
Instructions
Follow the instructions below.
- Add 5 drops of your first solution (liquid) to one of the holes in the dimple tile
- Add 2 drops of universal indicator.
- Use your pH chart to help you find the pH number.
- Write down your results before testing the next solution.
Notes - The pH Scale
Copy and complete the notes below into your notes.
Lesson 8 - Neutralisation
Learning Intentions
- Making neutral solutions from acids and alkalis.
Activity - Neatralisation
Equipment
- safety mat and glasses
- hydrochloric acid
- 10cm3measuring cylinder
- sodium hydroxide
- universal indicator
- test tube rack and a test tube.
Instructions
- Put 3cm3 of hydrochloric acid in a test tube.
- Add a few drops of indicator.
- Carefully, drop by drop, add the alkali (sodium hydroxide) until you neutralise the acid (ie it goes green). This can be rather tricky! Then stop
Results
Answer the following questions in sentences.
- How did you neutralise the acid?
- How did you know the acid had been neutralised?
- Describe any difficulties you had.
Activity - Indegestion Tablets
When people get heartburn or indigestion they often take antacid tablets to neutralise the acid in their stomach.
Equipment
- Safety mat and goggles
- 100cm3 measuring cylinder
- 250cm3 beaker
- glass stirring rod
- universal indicator
- mortar and pestle
- spatula
Instructions
- Put 100ml of “stomach acid” into a 250ml beaker.
- Add 5 drops of universal indicator.
- Slowly add the crushed antacid tablet.
- Stir the mixture until the solution is neutral (ie goes green).
Notes - Neutralisation
Copy and complete.
Lesson 9 - Making a Salt
Learning Intentions
- Know that a salt is formed when an acid neutralises an alkali.
- Know the word-equation for the neutralisation of acids by alkalis.
Activity - Making a Salt
Equipment
Collect the Following Equipment
- safety mat and goggles
- 100cm3 measuring cylinder
- pH paper
- dimple tile
- colour chart
- small beaker
- hydrochloric acid
- sodium hydroxide
- stirring rod
Neutralisation - Instructions
Watch your teacher demonstrate the experiment then follow the instructions on the worksheet
Write a sentence that describes how you made the neutral solution, and any problems you had.
Copy the diagram on side two of the sheet.
Copy the box.
Save your solution for the next lesson.
Evaporation - Instruction
Equipment
Collect the Following Equipment
- Bunsen burner
- Tripod stand
- Evaporation basin
Watch your teacher demonstrate evaporation then follow the instructions on the worksheet.
Notes - Neutralisation
When an acid and an alkali are mixed in the correct proportions, a neutral salt solution and water are formed - this is called neutralisation.
Word equation:
Acid + Alkali → salt + water
Sodium hydrixide + hydrochloric acid → sodium chloride + water
Lesson 10 - Acid Rain
Learning Intentions
- What is acid rain, and how is it made?
- How does acid rain affect buildings?
- What are the effects of acid rain on animals and plants?
- How can we make less acid rain?
How is acid rain formed?
Acid rain is caused by the gas sulphur dioxide which is produced when fossil fuels are burned.
It reacts with water in the atmosphere, then falls as 'acid rain'.
Power stations in Scotland burn coal to produce over 100,000 tonnes of sulphur dioxide every year.

Activity - Acid Rain Poster
Your task is to make a poster that answers one of the questions in the learning intentions.
You will find the following information helpful but you may also wish to do your own research.
Lesson 11 - The Effects of Acid Rain on Buildings
Learning Intentions
- To find out what happens when acid rain reacts with metal carbonates in building stones.
- To name the gas given off in this reaction
Activity - The reaction of metal carbonates with acid
Copy the table below into your notes.
| Metal Carbonate |
Acid Used |
Observation |
Gas Produced |
| Calcium carbonate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equipment
Collect the following equipment:
- Safety mat and goggles
- 3 x test tubes
- test tube rack
- delivery tube
- boiling tube
- hydrochloric acid
- limewater
- spatula
- metal carbonates
Instructions
- Put some limewater into a test tube.
- Place 1 spatula of calcium carbonate to a boiling tube add 2cm3of acid.
- Fit the delivery tube to the boiling tube.
- Test the gas released by bubbling it through limewater.
Results
Copy and complete the note below.
End of Topic Quiz





































